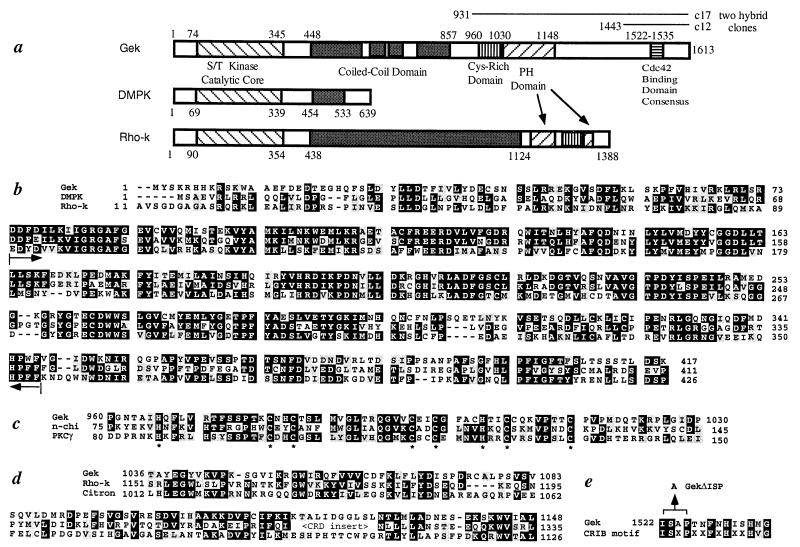
Figure 2.
Primary structure of Gek. (a) A schematic drawing of the Gek protein structure, with comparison to human DMPK (38) and bovine Rho-kinase (Rho-k) (25). Gek has four regions (448–589, 617–669, 685–738, and 784–857) that are predicted to form coiled-coil structures (score of 0.4 or above) (39). The lines above the Gek structure represent the original clones (c17 and c12) identified in the two-hybrid screen. (b) Sequence of the N terminus of Gek compared with DMPK and Rho-k. Brackets within the two arrows indicate the catalytic core of the kinase domain (20). Sequence similarities exist beyond the catalytic cores of these three proteins. (c) Sequence comparison of the Cys-rich domain of Gek with those of two phorbol ester binding proteins, n-chimerin (40), and protein kinase C γ (21). Conserved His and Cys residues are highlighted by ∗. (d) The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of Gek aligned with those of Rho-k (25) and Citron (41). Citron also shares general structural similarity with Gek yet no kinase domain was reported (41). Note that the PH domain of Rho-k is split by a Cys-rich domain. (e) The Cdc42-binding domain of Gek aligned with a recently identified Cdc42/Rac interactive binding consensus sequence (23). The position of the three amino acids deleted in GekΔISP is indicated. In all parts, the numbers represent that of amino acids within their respective proteins, whereas black and gray shadows represent identity and conservative changes of amino acids among different proteins, respectively.