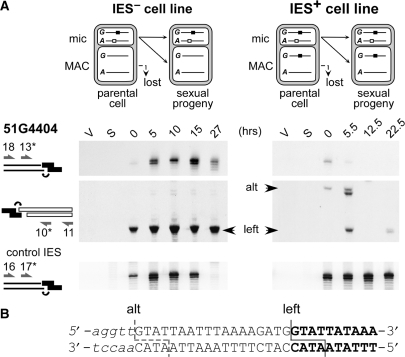
Figure 4.
Maternal control of IES end cleavage in an IES+ cell line. (A) LMPCR detection of DNA double-strand breaks at the left boundary of IES 51G4404 during autogamy of a wild-type IES− cell line (left) and its IES+ macronuclear variant (right). Top panels: broken chromosome ends revealed following ligation of linker I′/(GTAT)J′. Middle panels: broken IES ends analyzed with linker I′/(ATAC)J′. Flanking chromosomal sequences are drawn as thin lines, IES sequences as white rectangles and each linker is shown in black. Oligonucleotides are represented by arrows. Bottom panels: broken chromosome ends at the left boundary of control IES 51A2591 analyzed with linker I′/(GTAT)J′. (B) Sequence analysis of band ‘alt’ identified at the left end of IES 51G4404. Bold letters represent the sequence ligated to the linker in the wild-type LMPCR product (‘left’), additional nucleotides found in the ‘alt’ product are in uppercase and upstream flanking sequences in lower case. The positions of the deduced double-strand breaks are shown.