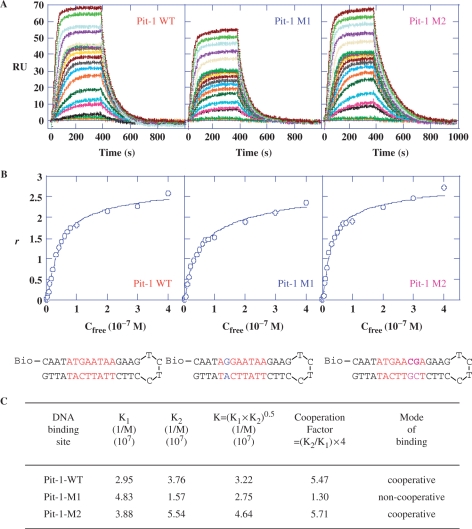
Figure 6.
SPR analysis of the DB293 interaction with wild-type or various mutated Pit-1 transcription factor binding sites. (A) SPR sensorgrams for binding of increasing concentrations of DB293 (1 nM to 0.4 µM) to the wild-type (WT) Pit-1 consensus-binding sites (red) or mutated sequences Pit-1-M1 (blue) or Pit-1-M2 (purple) sequences within biotinylated hairpin oligonucleotides in MES buffer, 25°C. The minimal consensus-binding sites are visualized in red. (B) Binding plots derived from SPR sensorgrams used to calculate the affinity constants for DB293 bound to the various sequences. Written in red are the specific consensus-binding sites with mutation points in blue (M1, removing the ATGA) or purple (M2, removing the AT-rich sequence 3′ to the ATGA). (C) Equilibrium constants for DB293 binding to Pit-1-WT, Pit-1-M1 and Pit-1-M2 sequences. The deduced cooperativity factor identifies the potential cooperativity of DB293 molecules for DNA binding. A weak nonspecific binding (factor of 10- to 50-fold less than the strong consensus binding) was also obtained but could not be accurately determined.