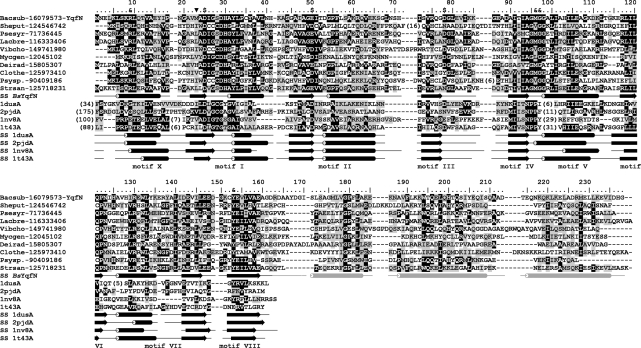
Figure 1.
Multiple sequence alignment of the YqfN/TrmK family. Only representative sequences are shown and named using a six-letter abbreviation for genus and species, e.g. Bacsub for B. subtilis, followed by the NCBI GI number. Full alignment is available as Supplementary Data 1. The amino acid residues of B. subtilis YqfN/TrmK are numbered. The template structures detected by FR and used for modeling are shown at the bottom, identified by their PDB accession numbers. Invariant and conserved residues are highlighted in black and dark grey, respectively. Secondary structures taken from the final model of YqfN/TrmK and observed in template structures are indicated as tubes and arrows (helices and strands, respectively). Secondary structure of YqfN/TrmK is colored black in regions based on conserved parts of the templates, while regions folded de novo are shown in light grey. Residues predicted to be involved in AdoMet binding (‘$’) or RNA binding and/or catalysis (‘&’) are indicated above the alignment. The previously proposed (apparently incorrect) N-terminal methionine is indicated by ‘inverted filled triangle’.