Abstract
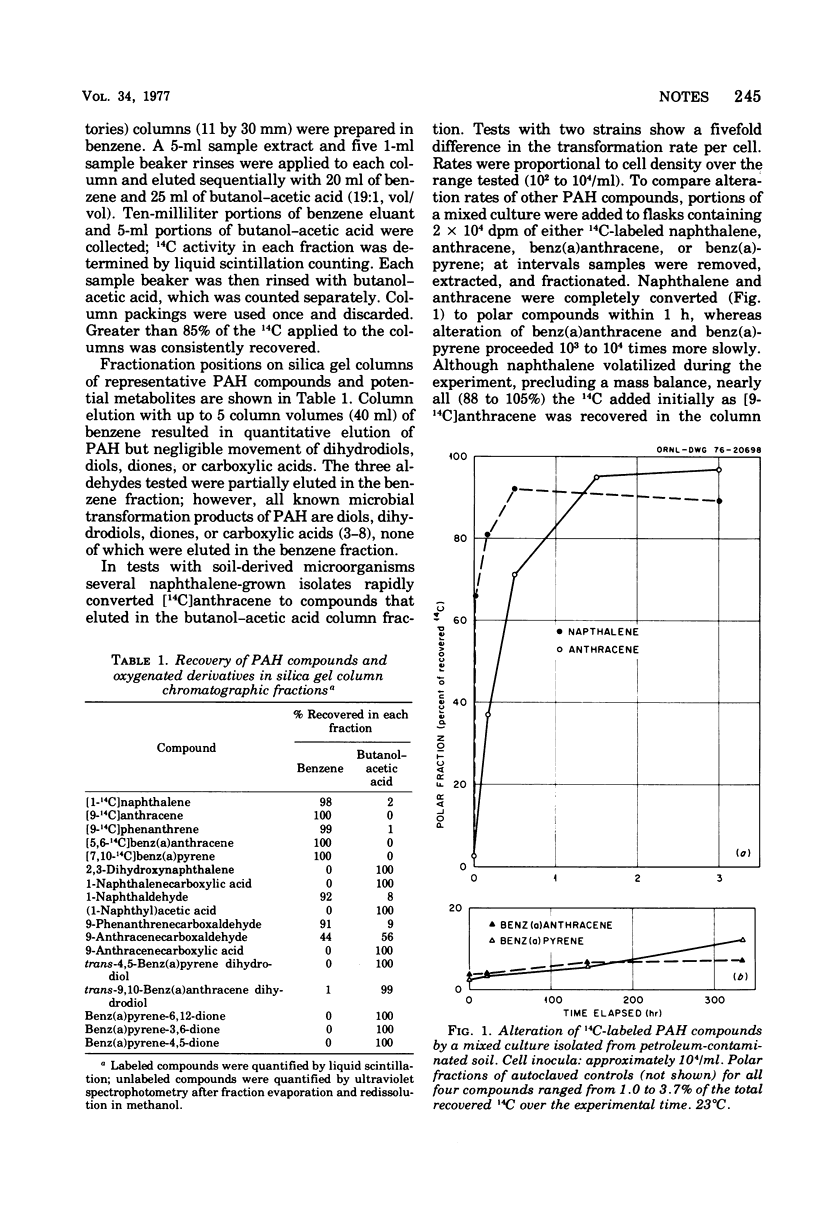
A chromatographic procedure has been developed for isolating and quantifying microbial transformation products of 14C-labeled polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Transformation rates of naphthalene, anthracene, benz(a)anthracene, and benz(a)pyrene by a mixed bacterial population have been measured. With this procedure, extremely slow or incomplete transformations may be quantified that would not be detectable by previously used techniques.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andelman J. B., Suess M. J. Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in the water environment. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(3):479–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnsley E. A. The bacterial degradation of fluoranthene and benzo[alpyrene. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jul;21(7):1004–1008. doi: 10.1139/m75-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. C., FERNLEY H. N., GRIFFITHS E. OXIDATIVE METABOLISM OF PHENANTHRENE AND ANTHRACENE BY SOIL PSEUDOMONADS. THE RING-FISSION MECHANISM. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:819–831. doi: 10.1042/bj0950819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Mahadevan V., Jerina D. M., Yogi H., Yeh H. J. Oxidation of the carcinogens benzo [a] pyrene and benzo [a] anthracene to dihydrodiols by a bacterium. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.1145203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T. Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds. Science. 1967 Sep 13;161(3846):1093–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Roberts R. L., Wells M. C., Kobal V. M. Oxidation of biphenyl by a Beijerinckia species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90828-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Jeffrey A. M., Gibson D. T. Cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene: a bacterial metabolite from naphthalene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jan;142(1):394–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaney G. W., Lutin P. A., Cibulka J. J., Hickerson L. H. Resistance of carcinogenic organic compounds to oxidation by activated sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1967 Dec;39(12):2020–2029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. Qualitative and quantitative studies on the metabolism of a series of aromatic hydrocarbons by rat-liver preparations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;19(3):795–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisler F. D., Zobell C. E. Microbial Utilization of Carcinogenic Hydrocarbons. Science. 1947 Nov 28;106(2761):521–522. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2761.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. D., Colwell R. R. Microbial petroleum degradation: use of mixed hydrocarbon substrates. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1053–1060. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1053-1060.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


