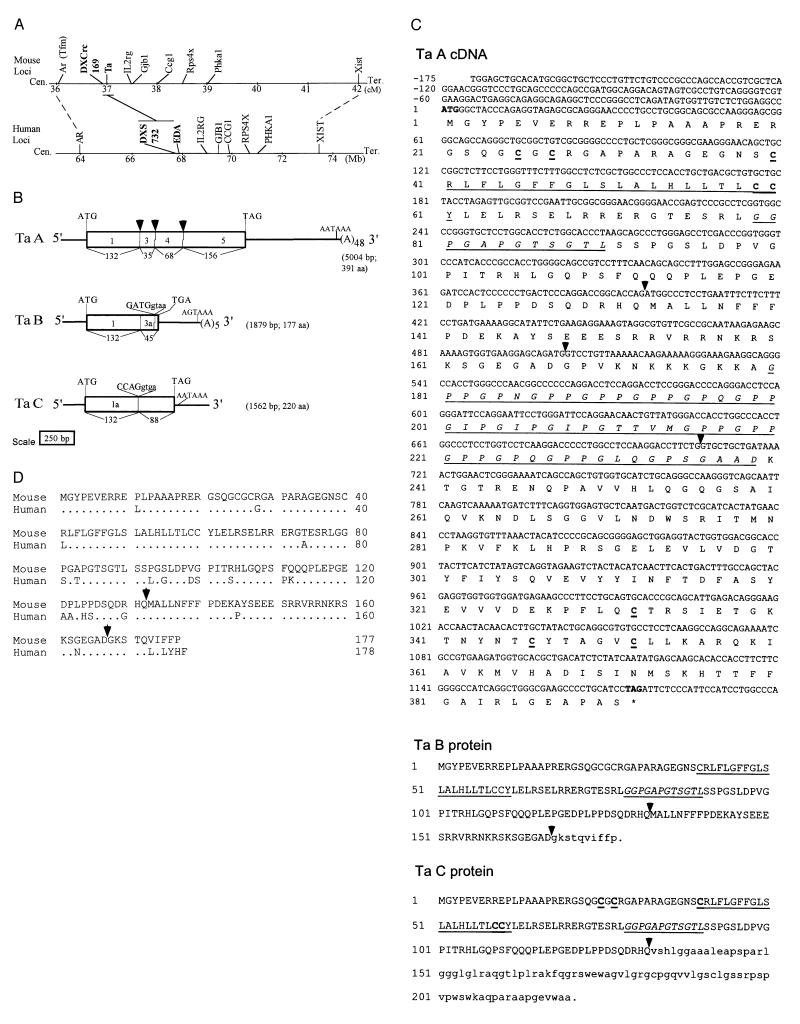
Figure 1.
(A) The location of the Tabby (Ta) locus on the mouse X chromosome genetic map (17) and EDA on a syntenic physical map of the human X chromosome (18). (B) Partial genomic organization of the Ta gene and corresponding transcript isoforms (Ta A, Ta B, and Ta C). Transcript size and protein length for each transcript are shown in brackets. Translated regions for exons (boxes) are drawn to scale and numbered. Note that no exon 2 corresponding to human EDA exon 2 has been detected in mouse. Numbers below each box represent amino acids encoded by the respective exon. Arrowheads show the locations of the exon–intron junctions in mouse genomic DNA. Split codons (see text) are shown by extensions within a box. Alternative exons (1a in Ta C and 3a in Ta B) are indicated. Potential splice site sequences are shown at 3′ ends of exon 1 and exon 3 in Ta C and Ta B transcripts. Sequence at the exon 4–intron junction (–TCTGgtgagt—) is not shown. Polyadenylylation site AATAAA or AGTAAA and poly(A) tail are indicated. (C) Nucleotide sequence (first 1,375 bp of 5,004-bp sequence, GenBank accession no. AF016628), predicted amino acid sequence of Ta A, and predicted peptide sequence of Ta B and Ta C. The predicted start of translation at +1 nucleotide with the in-frame stop codon (TAG) at nucleotides 1,174–1,176 yields an ORF of 1,176 bp that encodes a predicted protein of 391 amino acids in Ta A. A putative transmembrane domain is underlined, and the Gly-Xaa-Yaa collagenous repeats are in underlined italics. The locations of identified introns are indicated by arrowheads. Cysteine residues are indicated in underlined boldface. Amino acids in lowercase type are translated by in-frame adjacent intron sequences in alternatively spliced cDNAs Ta B and Ta C. (D) Amino acid sequence comparison of the mouse Ta B protein with its human EDA homologue. Identities are shown as dots.