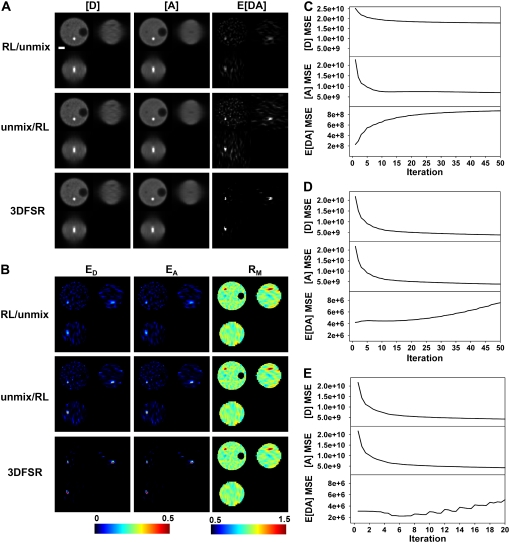
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of reconstruction techniques for noisy FRET data. Images were simulated from the model (with SNR ID = 10.4, IA = 24.9, IF = 10.3, for Poisson statistics), and three reconstruction approaches were applied to obtain estimates of [D], [A], and E[DA] (A) and ED, EA, and RM (B). Reconstruction with the overrelaxed RL algorithm followed by unmixing (RL/unmix) produced images that showed poor reconstruction of the FRET-positive compartment and many spurious signals in the cytosol (seen in the E[DA], ED, and EA images). Spectral unmixing before reconstruction by the RL algorithm (unmix/RL) produced estimates of E[DA] that showed improved reconstruction of the FRET-positive compartment; however, numerous spurious signals were also observed in E[DA], ED, and EA. 3DFSR outperformed direct application of the RL algorithm and produced excellent reconstruction of the [D], [A], and E[DA] concentrations as seen by the FRET-positive compartment approaching the expected FRET efficiency of 0.50 (dark red color in ED and EA) and the lack of spurious signals in E[DA], ED, and EA. The MSE between the reconstructed and simulated [D], [A], and E[DA] images indicated the convergence of the estimates to the original object for RL/unmix (C), unmix/RL (D), and 3DFSR (E). Scale bar is 1 μm. Slices are from the same planes as in Fig. 1.