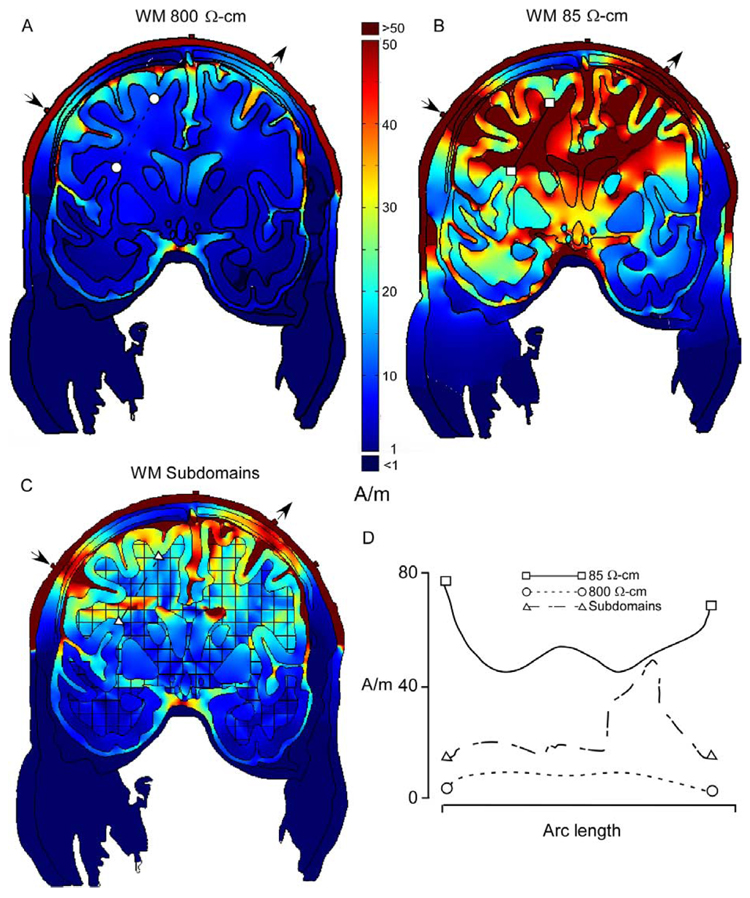
Fig. 2.
Current densities for the coronal section in Fig. 2, for models of current pathways across (A) 800 Ω cm, and parallel (B), 85 Ωcm, to white matter fiber tracts. (C) Model incorporating white matter anisotropies in resistivity. Resistivity was determined by dominant fiber orientation in each square of the grid. (D) Plots of current densities for sections (indicated by line segments) through white matter in (A), (B) and (C). Localization of current densities in white matter was greatest for the more realistic model in (C). Stimulation sites over the deep sulci are shown by the arrows.