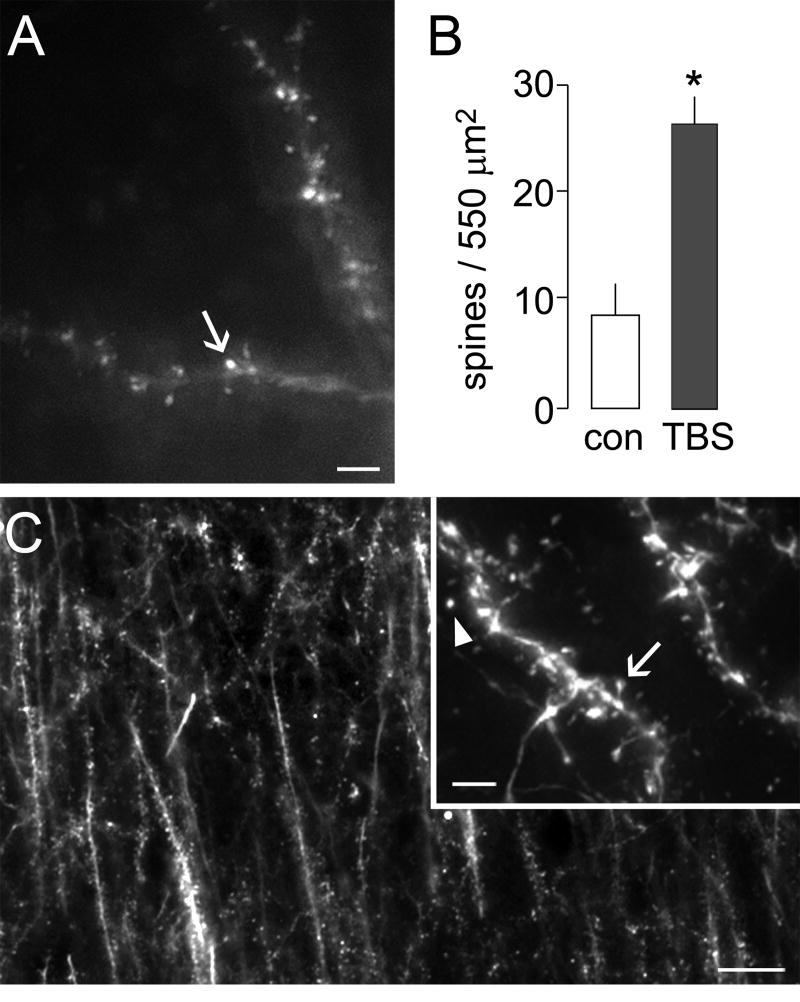
Figure 1. Theta burst stimulation induces actin polymerization in hippocampal dendritic spines.
Long-term potentiation was induced in adult hippocampal slices by theta burst stimulation (TBS) of Schaffer-collateral afferents to field CA1. F-actin was labeled in situ by application of rhodamine-phalloidin to identify stimulation effects on levels of polymerized actin in dendritic spines within the zone of potentiated synapses. (A) Photomicrograph shows labeling of F-actin by rhodamine-phalloidin applied through a patch-clamp electrode in a slice receiving theta stimulation. Numerous densely labeled spines are observed along the lengths of labeled dendrites (arrow). Calibration bar: 2 μm. (B) Plot shows the numbers of spines densely labeled with intracellular application of phalloidin to cells in control slices (con) and those receiving theta stimulation. Slices receiving theta stimulation showed nearly 3-fold greater numbers of densely labeled spines (*p<0.0001). (C) Low-power photomicrograph shows typical labeling of F-actin rich spines after extracellular application of fluorescent-tagged phalloidin at 20 min after theta stimulation. Calibration bar: 10 μm. Inset shows examples of isolated spines (arrowhead) and those with a clear head and neck attached to its parent dendrite (arrow). Calibration bar: 5 μm.