Abstract
This report from the Tuberculosis Chemotherapy Centre, Madras, describes the progress, over a 5-year period, of 341 patients with newly diagnosed, sputum-positive tuberculosis. All the patients were treated on a domiciliary basis. In the first year, the patients received, on the basis of random allocation, a standard regimen of isoniazid plus PAS or 1 of 3 regimens of isoniazid alone. Previous reports have shown that the response in the first year was substantially superior with the standard regimen, and that the bacteriological relapse rates in the second year were fairly similar for the 4 regimens. The findings in the present report extend the latter conclusion to the end of 5 years. Further, when considered together with the findings in an earlier study, they have shown that isoniazid, given as maintenance chemotherapy in the second year, was highly effective in preventing bacteriological relapse in patients who, at 1 year, had bacteriologically quiescent disease and no residual cavitation; the effect was, however, less marked in patients with residual cavitation at 1 year.
Patients who were clear-cut failures of the allocated chemotherapy and those who had a bacteriological relapse in the second or subsequent years were usually re-treated with streptomycin plus PAS or streptomycin plus pyrazinamide, and if this was ineffective, with cycloserine plus thioacetazone or cycloserine plus ethionamide.
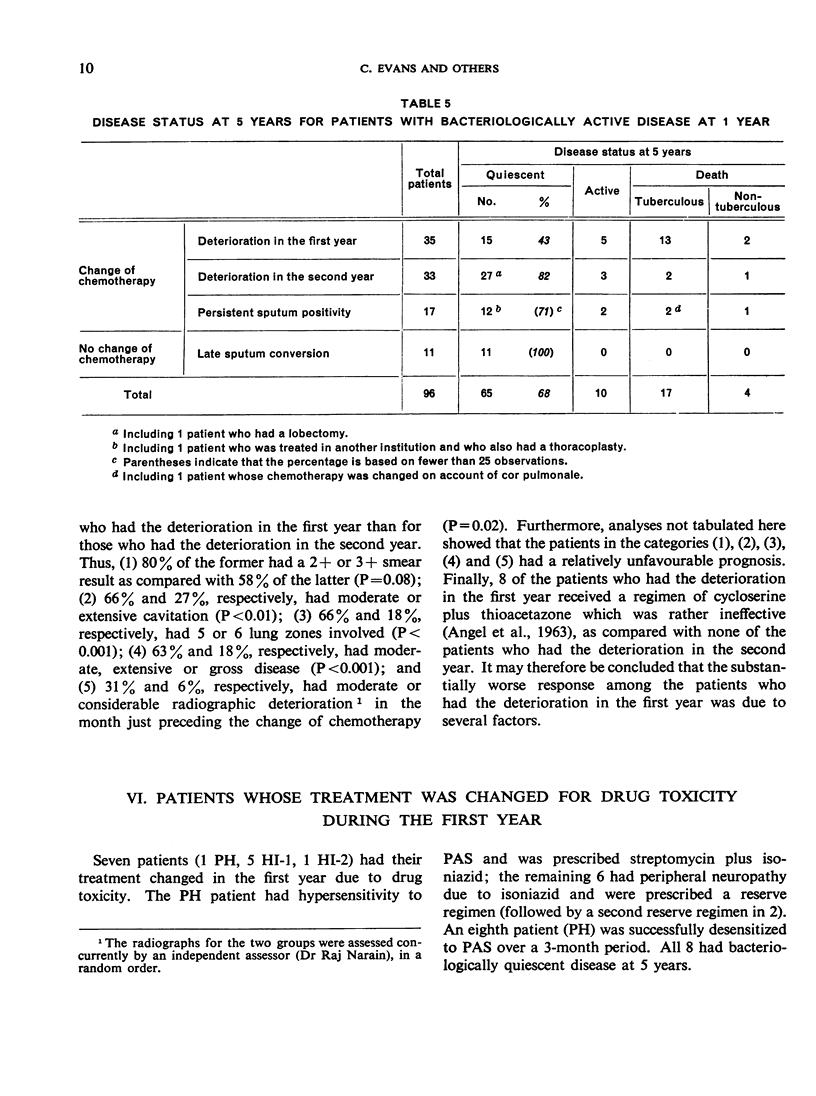
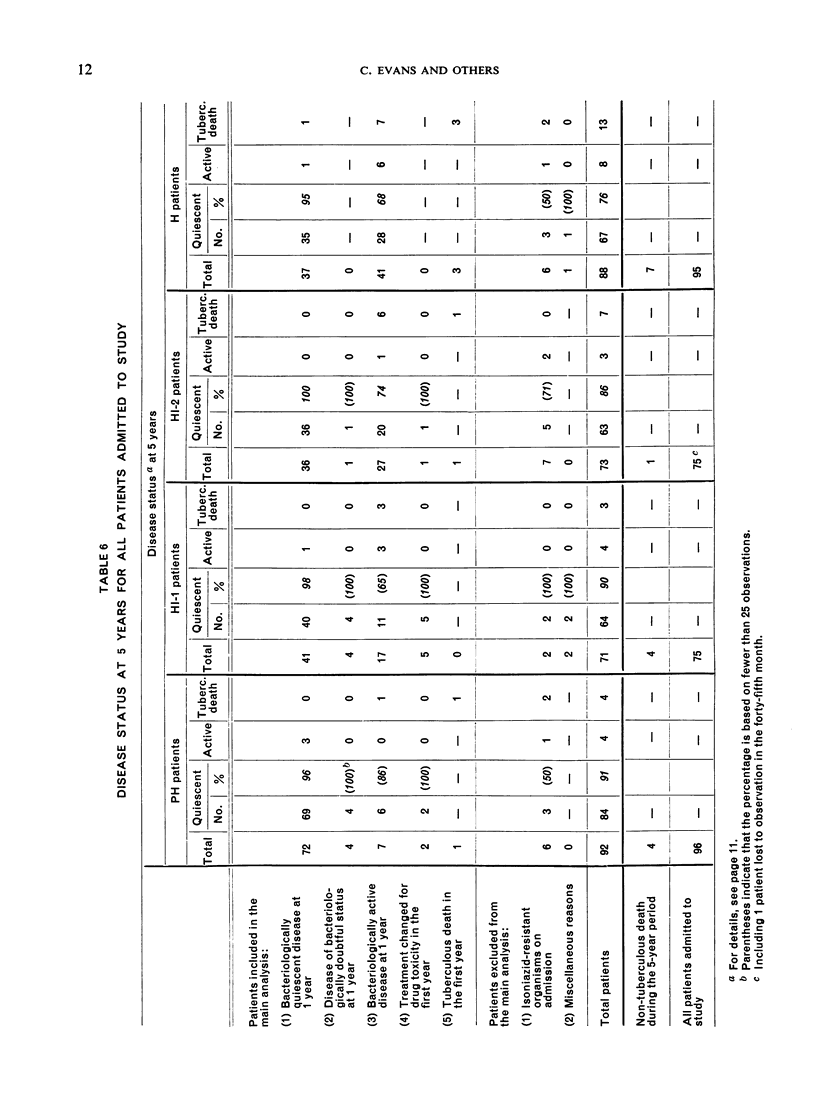
Considering the findings over the 5-year period for all patients, 16 died from non-tuberculous causes and 1 took his discharge prematurely. Of the remainder, 86% had bacteriologically quiescent disease at 5 years, 6% had bacteriologically active disease and 8% had died of tuberculosis. These findings confirm the value of well-organized domiciliary chemotherapy, which was established by an earlier report from the Centre, and are particularly encouraging for developing countries such as India, where tuberculosis is a major problem and resources are limited.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGEL J. H., BHATIA A. L., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., JANARDHANAM B., RADHAKRISHNA S., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., SELKON J. B., STOTT H., VELU S. A controlled comparison of cycloserine plus ethionamide with cycloserine plus thiacetazone in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis despite prolonged previous chemotherapy. Tubercle. 1963 Jun;44:215–224. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(63)80115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOONEIEF A. S., HITE K. E., BLOCH R. G. Indefinitely prolonged chemotherapy for tuberculosis; an appeal. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1955 Oct;96(4):470–477. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1955.00250150044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. J., Devadatta S., Fox W., Radhakrishna S., Ramakrishnan C. V., Somasundaram P. R., Stott H., Tripathy S. P., Velu S. A 5-year study of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in a concurrent comparison of home and sanatorium treatment for one year with isoniazid plus PAS. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(4):533–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTON P. W., LUTALO Y. K., WILLIAMS A. W., TONKIN I. M., FOX W. Acute pulmonary tuberculosis in East Africans: a controlled trial of isoniazid in combination with streptomycin or PAS. Tubercle. 1956 Jun;37(3):151–165. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(56)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDERMOTT W. Inapparent infection: relation of latent and dormant infections to microbial persistence. Public Health Rep. 1959 Jun;74(6):485–499. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., BHATIA A. L., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., NARAYANA A. S., SELKON J. B., VELU S. The course of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients excreting organisms which have acquired resistance. Response to continued treatment for a second year with isoniazid alone or with isoniazid plus PAS. Bull World Health Organ. 1962;26:1–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan C. V., Rajendran K., Mohan K., Fox W., Radhakrishna S. The diet, physical activity and accommodation of patients with quiescent pulmonary tuberculosis in a poor South Indian community. A four-year follow-up study. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(4):553–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VELU S., ANDREWS R. H., ANGEL J. H., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., GANGADHARAM P. R., NARAYANA A. S., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., SELKON J. B., SOMASUNDARAM P. R. Progress in the second year of patients with quiescent pulmonary tuberculosis after a year of domiciliary chemotherapy, and influence of further chemotherapy on the relapse rate. Bull World Health Organ. 1961;25:409–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VELU S., ANDREWS R. H., ANGEL J. H., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., JACOB P. G., NAIR C. N., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V. Streptomycin plus pyrazinamide in the treatment of patients excreting isonazid-resistant tubercle bacilli, following previous chemotherapy. Tubercle. 1961 Jun;42:136–147. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(61)80089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VELU S., DAWSON J. J., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., KULKARNI K. G., MOHAN K., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., STOTT H. A CONTROLLED COMPARISON OF STREPTOMYCIN PLUS PYRAZINAMIDE AND STREPTOMYCIN PLUS PAS IN THE RETREATMENT OF PATIENTS EXCRETING ISONIAZID-RESISTANT ORGANISMS. Tubercle. 1964 Jun;45:144–159. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(64)80072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


