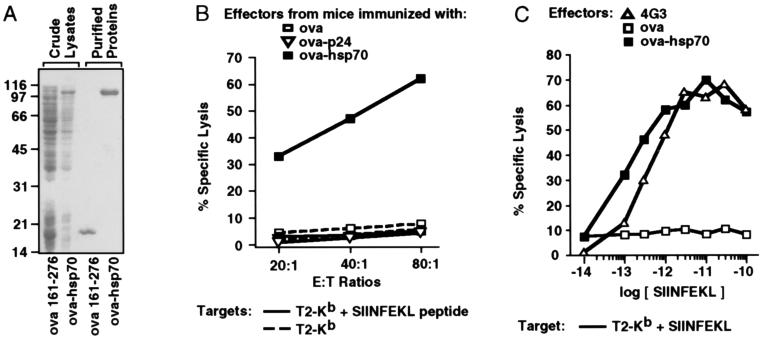
Figure 1.
A) Production of recombinant proteins. E. coli cell lysates and purified proteins were examined by SDS/PAGE and proteins were visualized by Coomassie staining. The gel contains crude extracts from isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG)-induced E. coli containing pKS28 (ova 161–276) and from IPTG-induced E. coli containing pKS76 (ova-hsp70), and the purified proteins ova 161–276 and ova-hsp70. Molecular weight markers (×10−3) are at left. (B) Generation of ovalbumin-specific CTL by immunization with ova-hsp70 fusion protein in saline. Mice were injected i.p. with 120 pmol of recombinant ovalbumin, ova-p24, or ova-hsp70 protein without adjuvant. The injections were repeated s.c. 2 weeks later. Mice were sacrificed 10 days after the boost and for each mouse group, 5–10 spleens were pooled and splenocytes from immunized mice were incubated for 6 days in the presence of irradiated E.G7-OVA cells without added interleukins. The splenocyte cultures derived from mice immunized with ovalbumin □, ova-p24 ▿, or ova-hsp70 ▪ were then used as effector (E) cells in a standard cytotoxicity assay. The following 51Cr-labeled target (T) cells were used: T2-Kb cells (broken line) and T2-Kb pulsed with SIINFEKL peptide (solid line) at 300 μg/ml. (C) SIINFEKL peptide titration. T2-Kb cells were incubated with the indicated molar concentrations of SIINFEKL peptide for 45 min for use as target cells in a CTL assay. The effector cells primed with ovalbumin □ or ova-hsp70 ▪ as described above were used at an E:T ratio of 80:1. The 4G3 CTL clone ▵ was used at an E:T of 5:1.