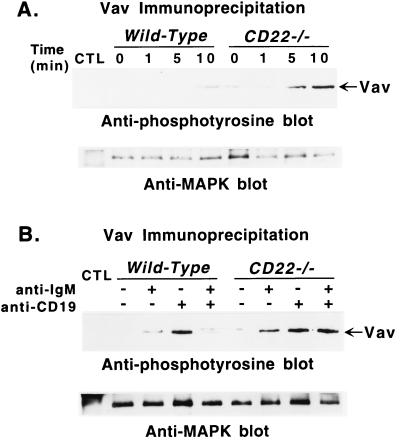
Figure 4.
Tyrosine phosphorylation of Vav after (A) ligation of CD19 or (B) coligation of BCR and CD19 in B cells from CD22-deficient mice and wild-type littermates. (A) Purified splenic B cells were incubated with either medium or optimal concentrations (60 μg/ml) of anti-CD19 antibodies. Cells (107) were removed from the cultures at the indicated times and solubilized. (B) B cells also were stimulated by suboptimal concentrations of either anti-CD19 antibodies (10 μg/ml), or anti-IgM antibodies (10 μg/ml), or both, as indicated, for 5 min before solubilization. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Vav antibodies, plus anti-MAPK antibodies or normal rabbit serum (CTL) as in Fig. 2. Immunoprecipitated proteins were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and transferred onto a membrane for subsequent anti-phosphotyrosine immunoblotting (Upper). All blots were subsequently stripped of anti-phosphotyrosine antibody and reprobed with anti-MAPK antibodies to quantify the amount of proteins within the immunoprecipitates (Lower). These results are representative of those obtained with at least three littermate pairs of mice.