Abstract
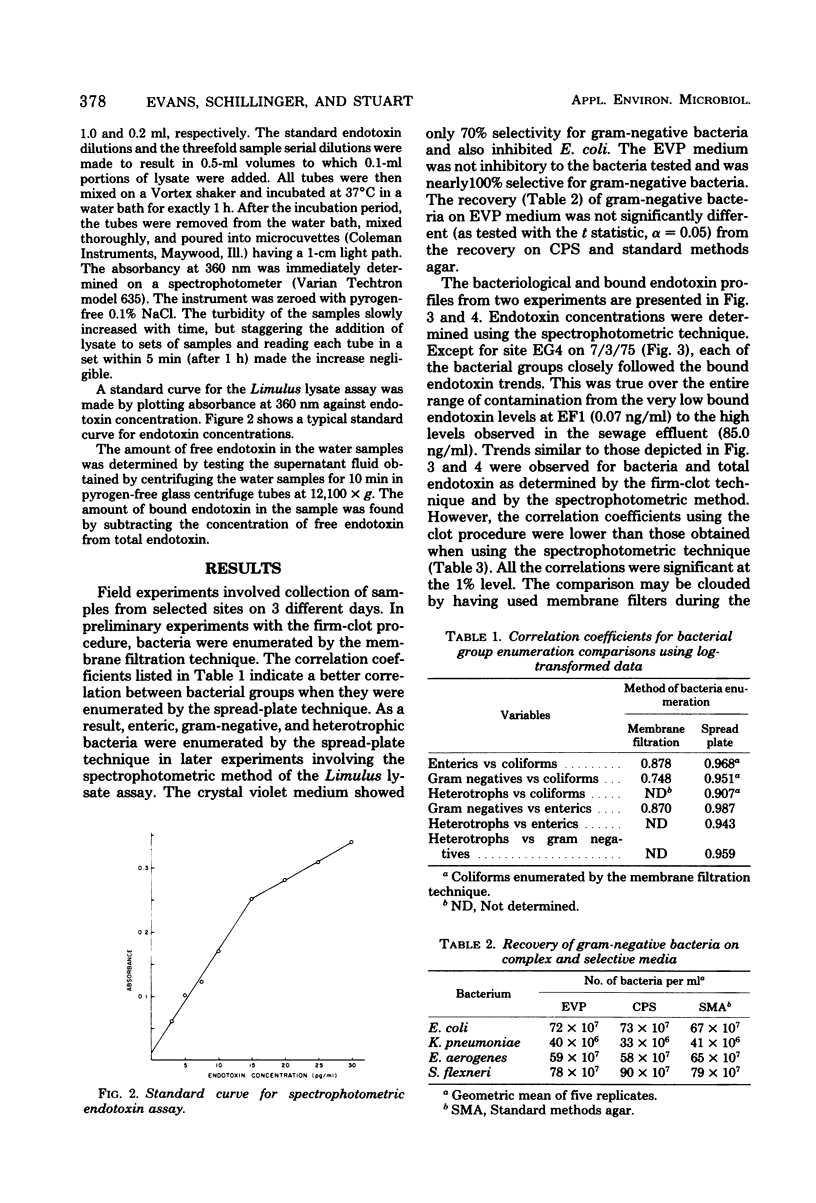
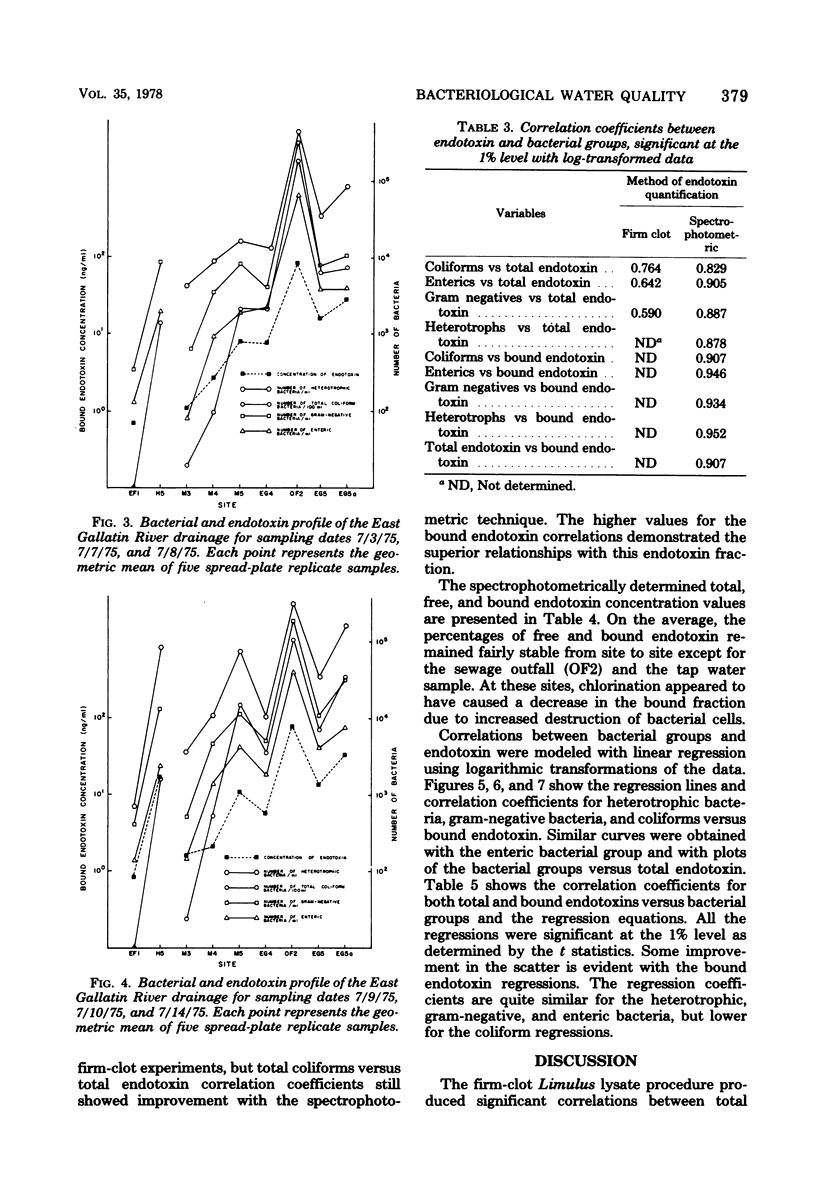
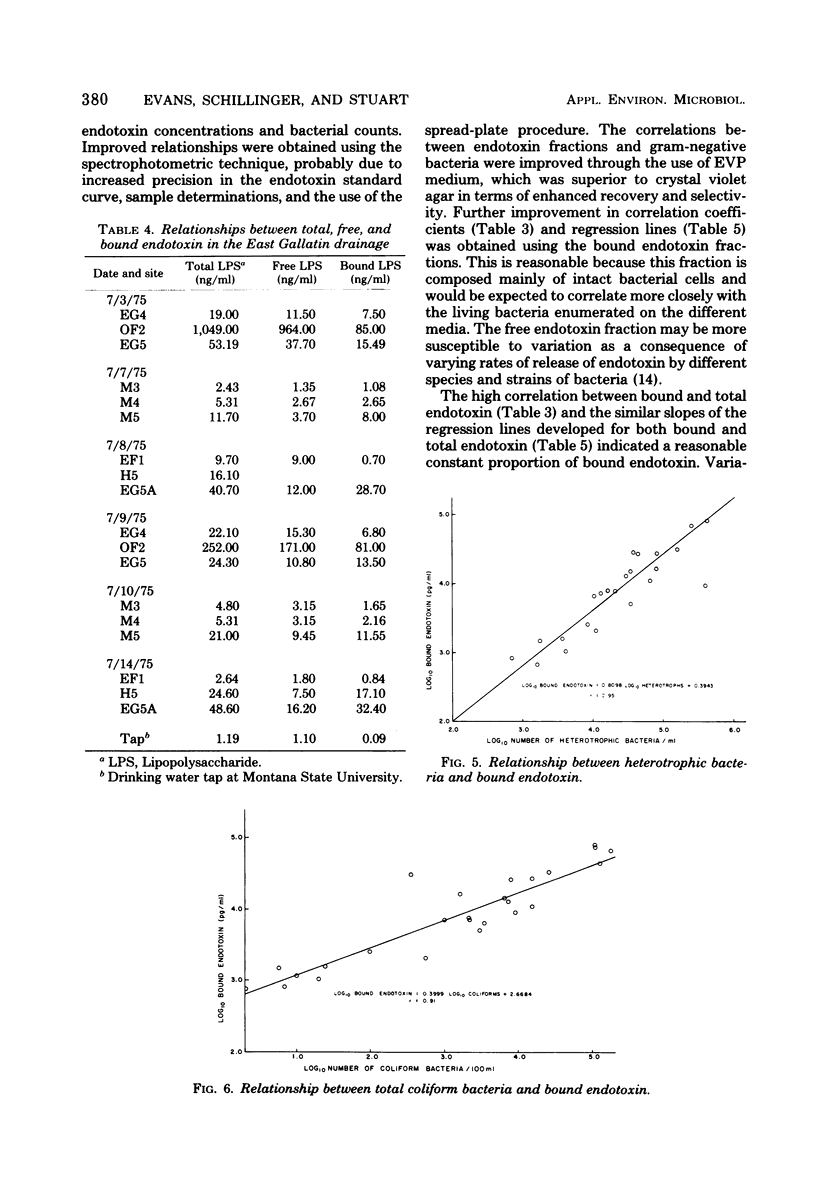
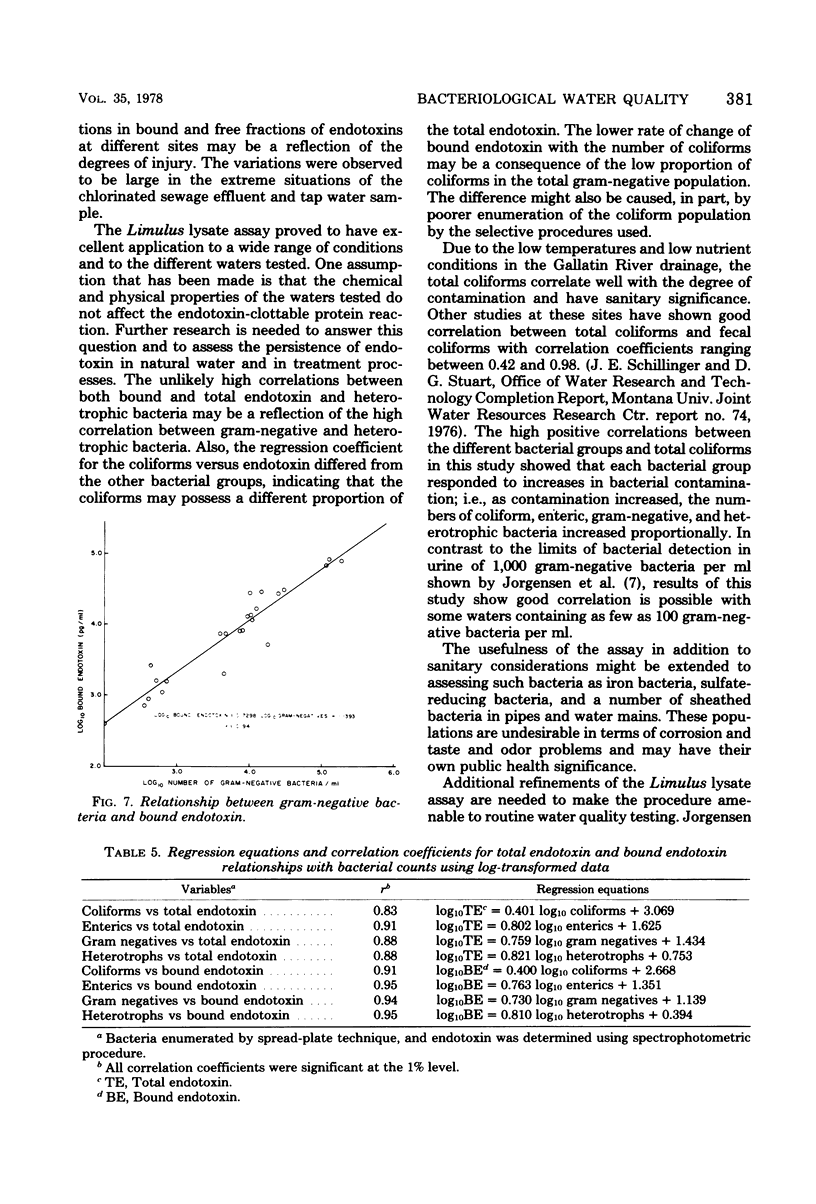
The Limulus lysate assay was used to measure the endotoxin content in stream water and was found to reflect the degree of bacterial contamination as measured by coliform, enteric, gram-negative, and heterotrophic bacteria. The firm-clot method was found to be a less sensitive and reproducible technique for the detection of endotoxin than was the spectrophotometric modification of the Limulus lysate assay. Bound endotoxin, as determined by the spectrophotometric modification of the Limulus lysate assay, was found to be a better measure of the endotoxin associated with bacterial cells than was total endotoxin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luzio N. R., Friedmann T. J. Letter: Bacterial endotoxins in the environment. Nature. 1973 Jul 6;244(5410):49–51. doi: 10.1038/244049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. Letter: Limulus assay for gram-negative endotoxin. Lancet. 1974 Jun 22;1(7869):1295–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Lee J. C., Pahren H. R. Rapid detection of bacterial endotoxins in drinking water and renovated wastewater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):347–351. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.347-351.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Smith R. F. Preparation, sensitivity, and specificity of Limulus lysate for endotoxin assay. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.43-48.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITSKY W., MALLMANN W. L., FIFIELD C. W. Ethyl violet selective dye for the isolation of gram-negative bacteria. Stain Technol. 1952 Sep;27(5):229–232. doi: 10.3109/10520295209105082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Bang F. B. Clottable protein in Limulus; its localization and kinetics of its coagulation by endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold R. B., Fine J. A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):334–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. D., Jr, Watson S. W. Factors affecting the sensitivity of Limulus lysate. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.1023-1026.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Heymer B., Schleifer K. H., Haferkamp O. Investigations on the specificity of the Limulus test for the detection of endotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):867–871. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.867-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Galanos C., Kinsky S., Bradshaw R. A., Wessler S., Lüderitz O., Sarmiento M. E. Picogram-sensitive assay for endotoxin: gelation of Limulus polyphemus blood cell lysate induced by purified lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


