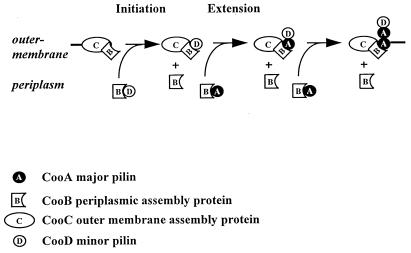
Figure 4.
Model of CS1 pilus assembly. CooB chaperone binds to CooC in the outer membrane to maintain its conformation and prevent its degradation. CooB also binds to the major and minor pilins, CooA and CooD, respectively, to guide their folding and/or inhibit pilin-pilin interactions leading to aggregation and degradation. A CooB–CooD complex initiates assembly by binding to CooC; CooB is displaced and is recycled into the periplasm where it may interact with other pilins. CooB–CooA complexes displace CooD from CooC, replacing it with CooA. Repeated interactions between CooB–CooA complexes and CooC allow incorporation of CooA at the base of the pilus and extension of the pilus rod.