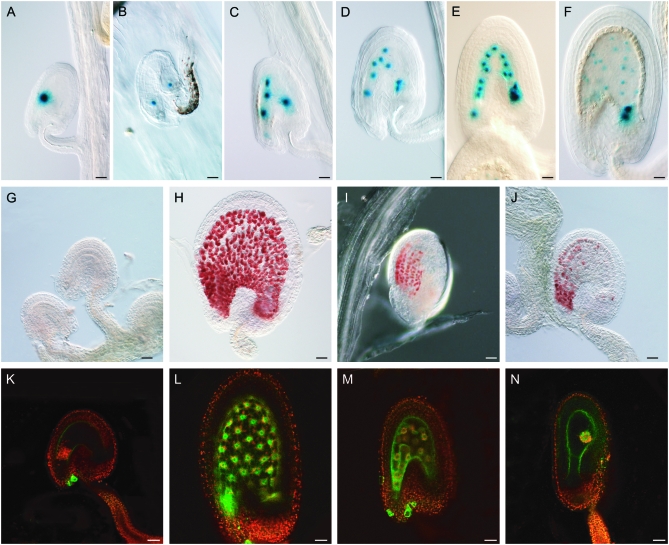
Figure 1.—
Endosperm characteristics of autonomously proliferating central cell nuclei. DIC light and confocal laser scanning (CLS) micrographs of developing double-fertilized (with wild-type pollen) and single-fertilized (with cdka;1 pollen) seeds. (A–F) Histochemical detection of GUS activity in seeds expressing a maternal FIS2-GUS construct (in the C24 ecotype) and pollinated with cdka;1 mutant pollen (A–E) or with wild-type pollen (F). The division pattern and nuclear migration of autonomous endosperm in cdka;1 fertilized seeds is similar to that seen in double-fertilized wild-type seeds. (A) FIS2-GUS expression in central cell nucleus (fused polar nuclei). (B) After the first division, one nucleus moves to the chalazal part of the seed. (C) Second division. (D) Third division. (E) Fourth division. (F) Fifth division cycle of an endosperm fertilized with wild-type pollen. (G–J) Detection of proanthocyanidin accumulation by vanillin staining in unpollinated Sha ovules or fertilized seeds at 3 DAP. (G) No proanthocyanidin can be detected in unfertilized Sha ovules. (H) Sha seeds fertilized with wild-type pollen accumulate proanthocyanidin in the endothelium. (I) Col-0 seeds fertilized with cdka;1 mutant pollen also start synthesizing proanthocyanidin. (J) Even seeds with little or nonproliferating central cell nuclei—as seen, for example, here in Sha fertilized with cdka;1 mutant pollen—are vanillin positive. (K–N) CLS micrographs of seeds or ovules containing the KS22 endosperm marker construct at 3 DAP, green GFP from the marker construct, red autofluorescence of plastids. (K) No GFP could be detected in an unpollinated wild-type C24 central cell. (L) Seeds fertilized with wild-type pollen showing expressing of the KS22 GFP reporter in the endosperm nuclei. (M) The autonomous endosperm in seeds fertilized with cdka;1 mutant pollen express GFP, even in cases where the central cell nucleus has not divided (N). All pictures are oriented such that the micropylar pole with the developing embryo points to the left and the chalazal pole of the seed to the right. Bars, 10 μm.