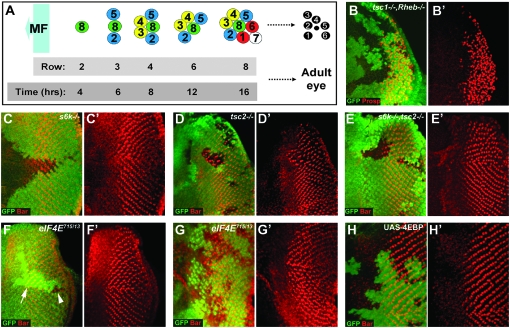
Figure 1.—
InR and TOR signaling act through S6K, but not eIF4E to control the timing of neuronal differentiation. (A) Schematic showing the spatiotemporal nature of PR differentiation in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc. MF, morphogenetic furrow. (B and B′) tsc12G3, Rheb2D1 double-mutant clones have an identical delay in differentiation (stained for Prospero expression, shown in red) to Rheb2D1 clones (Figure 2C). (C and C′) Loss of S6k causes a slight delay in the differentiation of PR 7 and cone cells (stained for Bar expression, shown in red). (D and D′) tsc2 (gig56) clones cause precocious differentiation of PRs 1 and 6 (stained for Bar expression, shown in red). (E and E′) The precocious differentiation phenotype of tsc2 cells is suppressed in tsc2 (gig192), s6k11 clones (Bar staining in red). (F and G) eIF4E715/13 LOF clones inhibit growth resulting in small clones, compare clone (arrowhead) to twin spot (arrow) size in F, but do not affect differentiation in posterior clones generated using hs-flp (F and F′) or clones close to the MF, generated using ey-flp (G and G′), (Bar staining in red). (H and H′) overexpression of 4EBP (shown by the presence of GFP staining) does not have any affect on differentiation of PRs 1 and 6 (stained for Bar expression, shown in red). LOF clones in B–G are marked by the loss of GFP (shown in green). Anterior is to the left in all panels.