Figure 6.
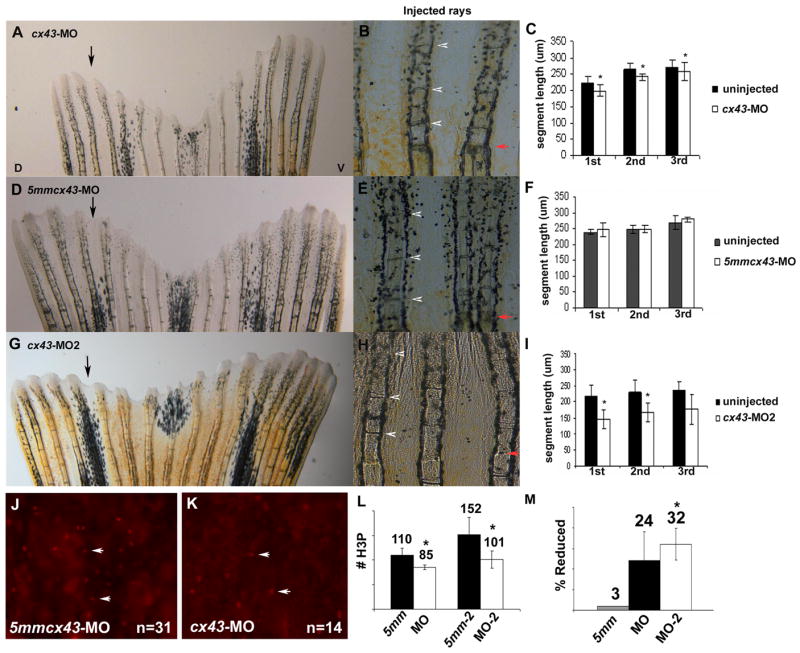
Knockdown of Cx43 recapitulates the sof phenotype. Wild-type fins were injected/electroporated in dorsal fin rays with either targeting morpholino (cx43-MO, cx43-MO2) and the respective control morpholino. The ventral side of the fin was electroporated only. At 4 dpe, segment length was measured for the first three newly formed segments for each fin ray. (A) Fin electroporated with 1.2 mM cx43-MO. (B) Segment size was measured for both injected and uninjected fin rays. (C) Graph comparing segment length (μm) for the cx43-MO and the uninjected rays. There is a significant difference in segment length for all three segments (p < .01). (D) Fin electroporated with 1.2 mM 5mmcx43-MO. (E) Segment size was measured for both injected and uninjected fin rays. (F) Graph comparing segment length (μm) for the 5mmcx43-MO and the uninjected rays. There is no significant different in segment length (p = 0.25, p = 0.94, p = 0.08, respectively). (G) Fin electroporated with 1.2 mM cx43-MO2. (H) Segment size was measured for both injected and uninjected fin rays. (I) Graph comparing segment length (μm) for the cx43-MO2 and the uninjected rays. There is a significant difference in segment length for all three segments (p < 0.01). Black arrows indicate the injected lobe, red arrows indicate the amputation plane, arrowheads designate newly formed joints. (J–L) Wild-type fins were injected/electroporated with either targeting or control morpholinos, harvested at 1 dpe and processed for H3P detection. Representative images of H3P positive cells are shown in J,K. (J) Dorsal rays were injected/electroporated with 5mmcx43-MO. (K) Ventral fin rays were injected/electroporated cx43-MO. (L) A significant reduction in H3P number was observed for either targeting morpholino (cx43-MO, p < 0.01 and cx43-MO2, p = 0.01) when compared to their corresponding controls. (M) The cx43-MO2 appears more effective at cx43 gene knockdown than cx43-MO since the percentage of H3P positive cells was more greatly affected when the cx43-MO2 was used (p < 0.05 when comparing the percent reduction of H3P positive cells of cx43-MO and cx43-MO2).
