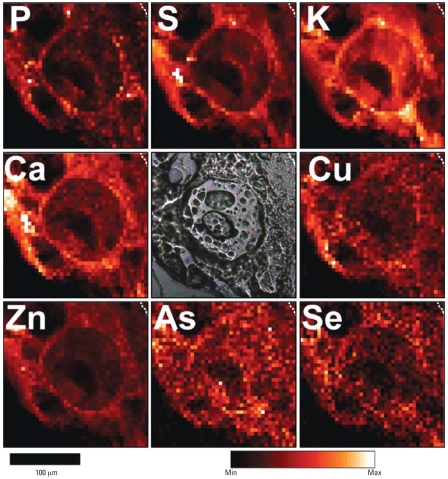
Figure 1.
Micro-XRF element maps of hyperplastic epidermis taken from the skin of a mouse exposed to UVR and As(III) for 182 days. Dashed lines in upper right corners demarcate the boundary between epidermis and a tiny amount of dermis. Abbreviations: Max, maximum; Min, minimum. A phase-contrast image in the central panel shows a large, circular nucleus containing a large nucleolus. Other pocklike structures are artifacts of desiccation. The giant cell is a typical “sunburn” cell with a huge nucleus and a barely perceptible cytoplasm. The nucleolus, being mostly RNA, contains little, if any, of the sampled elements. Near the large cell are several normal-sized epidermal cells. The elements sulfur, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, copper, zinc, and Se are generally concentrated in the membrane regions at the peripheries of the cells.