Abstract
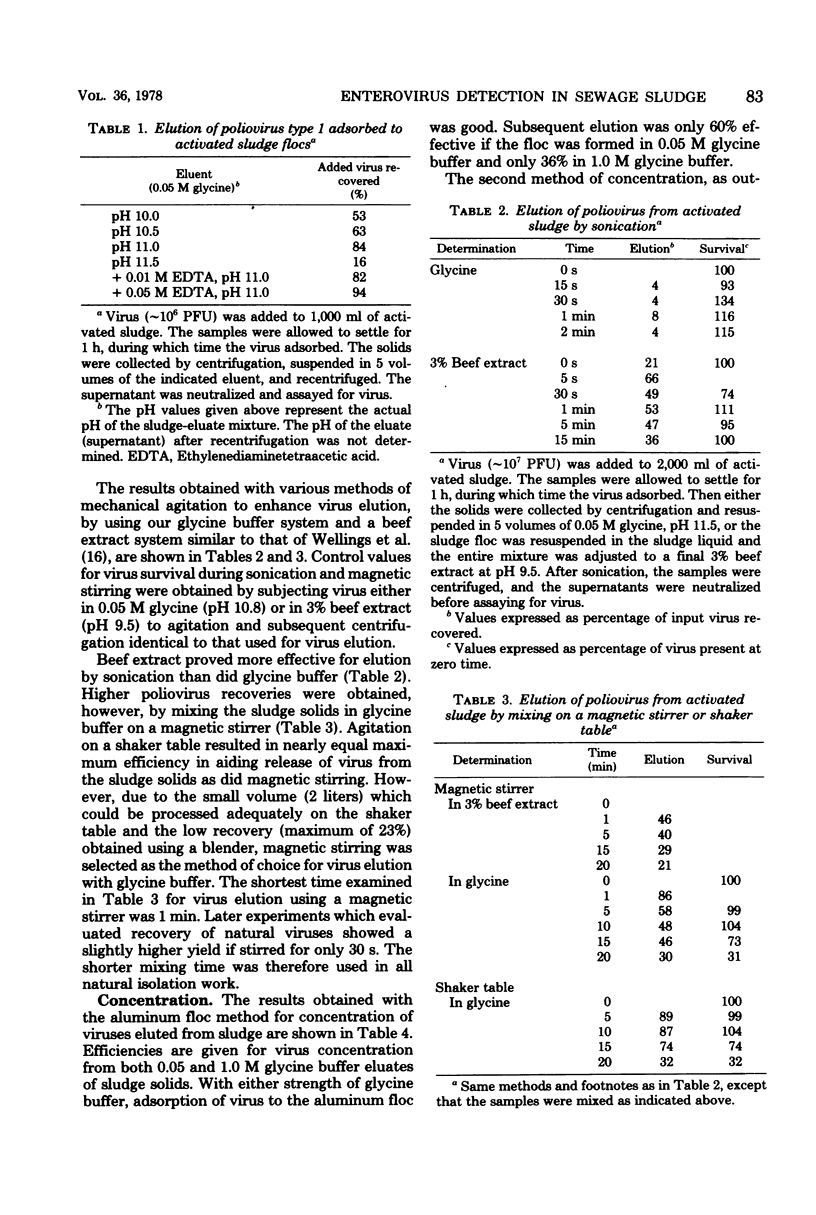
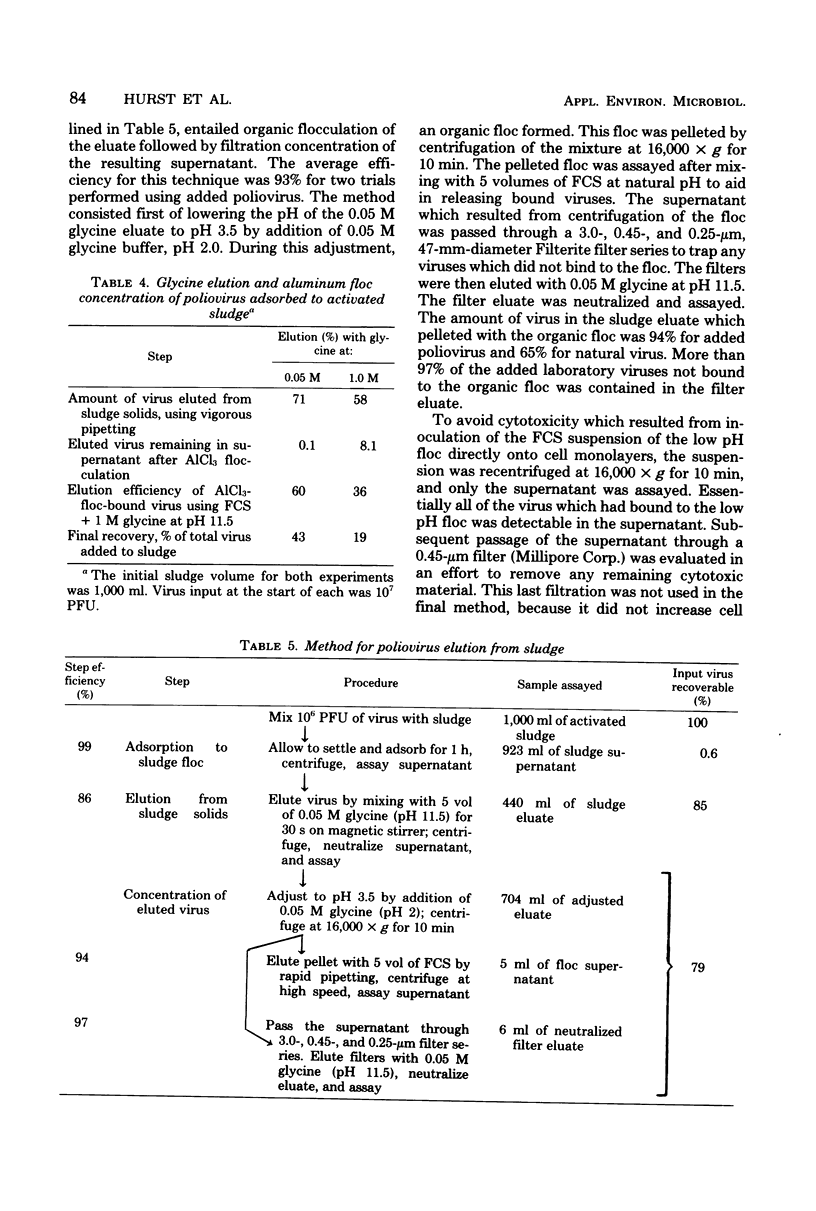
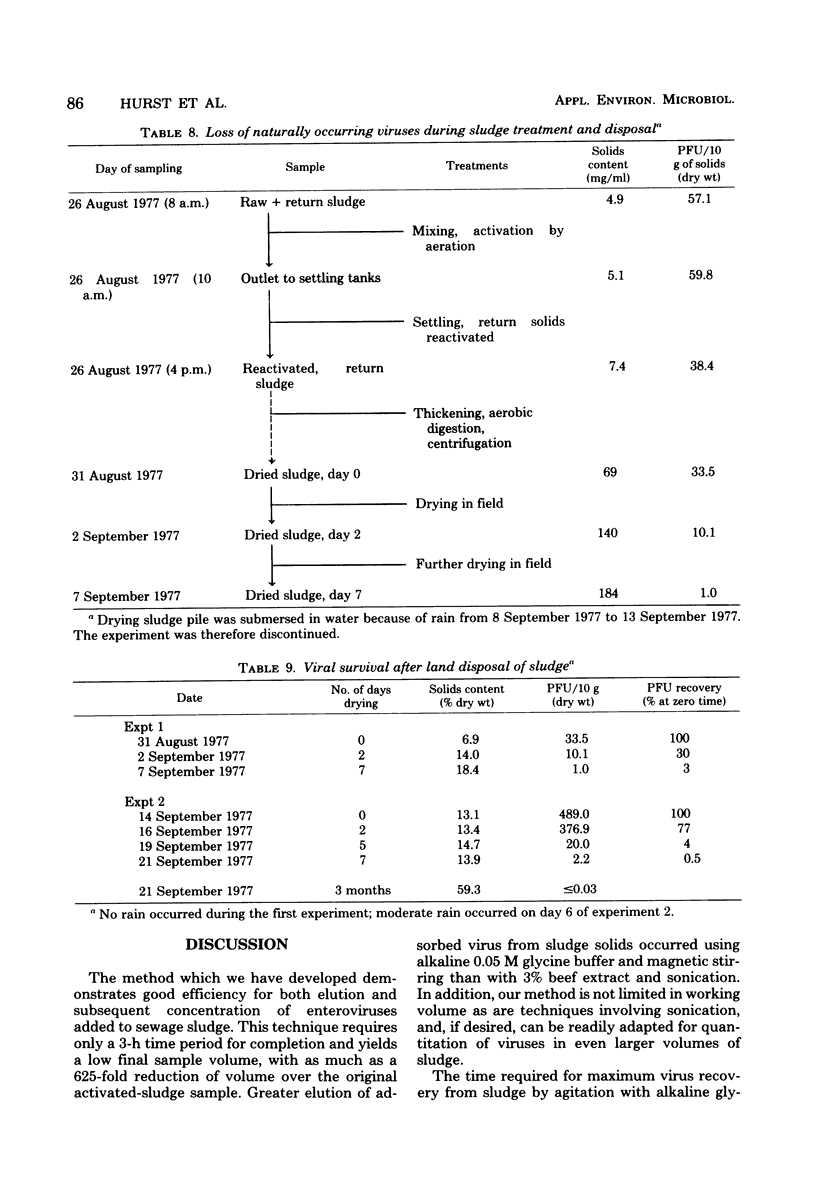
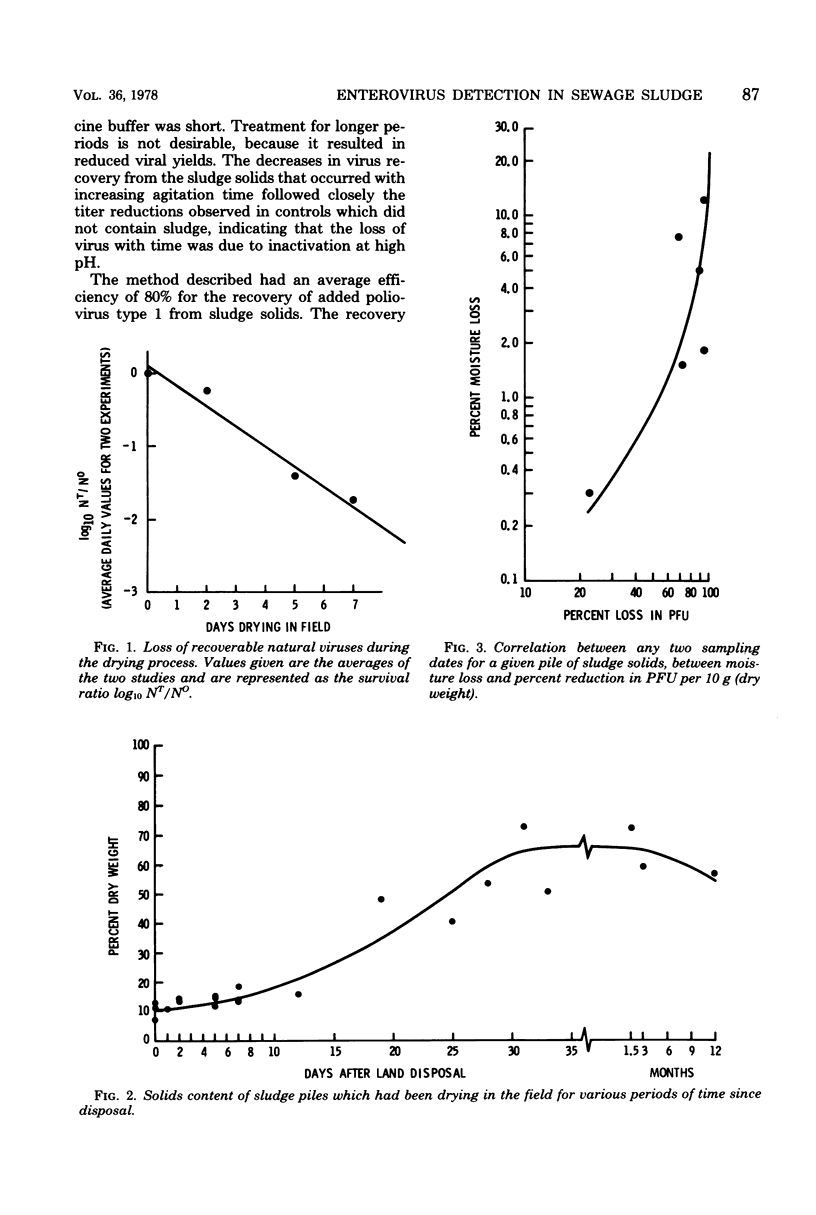
The development and evaluation of methods for the quantitative recovery of enteroviruses from sewage sludge are reported. Activated sewage sludge solids were collected by centrifugation, and elution of the solid-associated virus was accomplished by mechanical agitation in glycine buffer at pH 11.0. Eluted viruses were concentrated either onto an aluminum hydroxide floc or by association with a floc which formed de novo upon adjustment of the glycine eluate to pH 3.5. Viruses which remained in the liquid phase after lowering the pH of glycine eluate were concentrated by adsorption to and elution from membrane filters. The method of choice included high pH glycine elution and subsequent low pH concentration; it yielded an efficiency of recovery from activated sludge of 80% for poliovirus type 1, 68% for echovirus type 7, and 75% for coxsackievirus B3. This method was used to study the survival of naturally occurring virus in sludge at a sewage treatment plant and after subsequent land disposal of the solids after aerobic digestion. Reduction of enterovirus titers per gram (dry weight) of solids were modest during sludge activation but increased to a rate of 2 log 10/week after land disposal.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farrah S. R., Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from estuarine water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1192-1196.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Smith E. M., Melnick J. L. Development of a quantitative method for detecting enteroviruses in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):158–163. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.158-163.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Rennick V., Hampil B., Schmidt N. J., Ho H. H. Lyophilized combination pools of enterovirus equine antisera: preparation and test procedures for the identification of field strains of 42 enteroviruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(3):263–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattar S. A., Westwood J. C. Comparison of four eluents in the recovery of indigenous viruses from raw sludge. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;22(10):1586–1589. doi: 10.1139/m76-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Henderson M., Melnick J. L. Enterovirus concentration on cellulose membranes. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):476–480. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.476-480.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Inactivation of enteric viruses in wastewater sludge through dewatering by evaporation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.564-570.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Inactivation of poliovirus in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):921–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.921-930.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W. Demonstration of solids-associated virus in wastewater and sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):354–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.354-358.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


