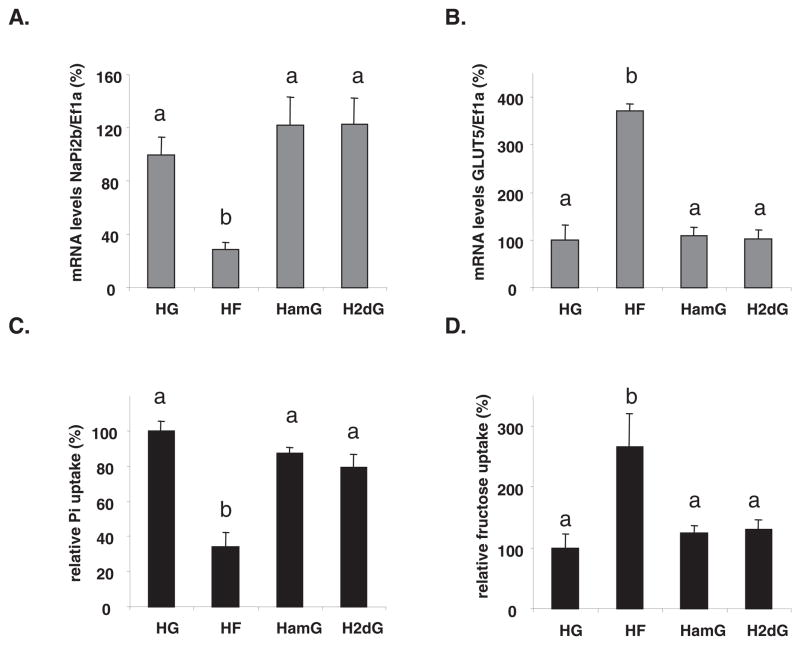
FIGURE 2.
Dependence to sugar type of the luminal sugar-modulated sodium-phosphate cotransporter (NaPi-2b) expression and activity. The small intestine was perfused with 100 mmol/L glucose, fructose, or glucose analogs in Krebs Ringer Bicarbonate solution. HG, high D-glucose; HF, high D-fructose; HamG, high α-methyl-D-glucose [SGLT1 (sodium-glucose cotransporter type 1) substrate, nonmetabolized in the enterocyte]; H2dG, high 2-deoxy-glucose (poorly transported sugar that is partly phosphorylated in the cell). A: NaPi-2b mRNA abundance. B: GLUT5 (glucose transporter 5) mRNA abundance. C: Inorganic phosphate (Pi) relative uptakes. D: Fructose relative uptakes. mRNA concentrations and relative uptakes in HG-perfused pups were designated as 100% to normalize other groups to this value. Error bars represent means ± SEMs (n = 5). Different letters denote significant (P <0.05) differences (one-factor ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). NaPi-2b mRNA concentrations and Pi uptake were down-regulated ≈3-fold in the HF-perfused relative to the HG-, HamG-, and H2dG-perfused small intestine. Ef1a, elongation factor 1α.