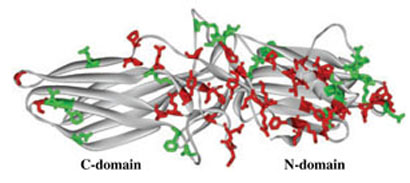
Fig 5.
Conserved residues on the non-receptor-binding side of arrestin molecule. Comparable binding of all four vertebrate arrestins to c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Mdm2 suggests that the residues on the non-receptor-binding side that are either conserved throughout the arrestin family (side chains high-lighted in red) or conservatively substituted in different arrestin subtypes (side chains highlighted in green) mediate these interactions. These residues form three ‘patches’: two relatively large ones on the distal N-domain and near the center on the molecule and a small one on the distal C-domain. Note that a considerable portion of the C-domain does not carry conserved residues, which makes this area a likely candidate for the binding of subtype-specific arrestin partners.