Figure 1.
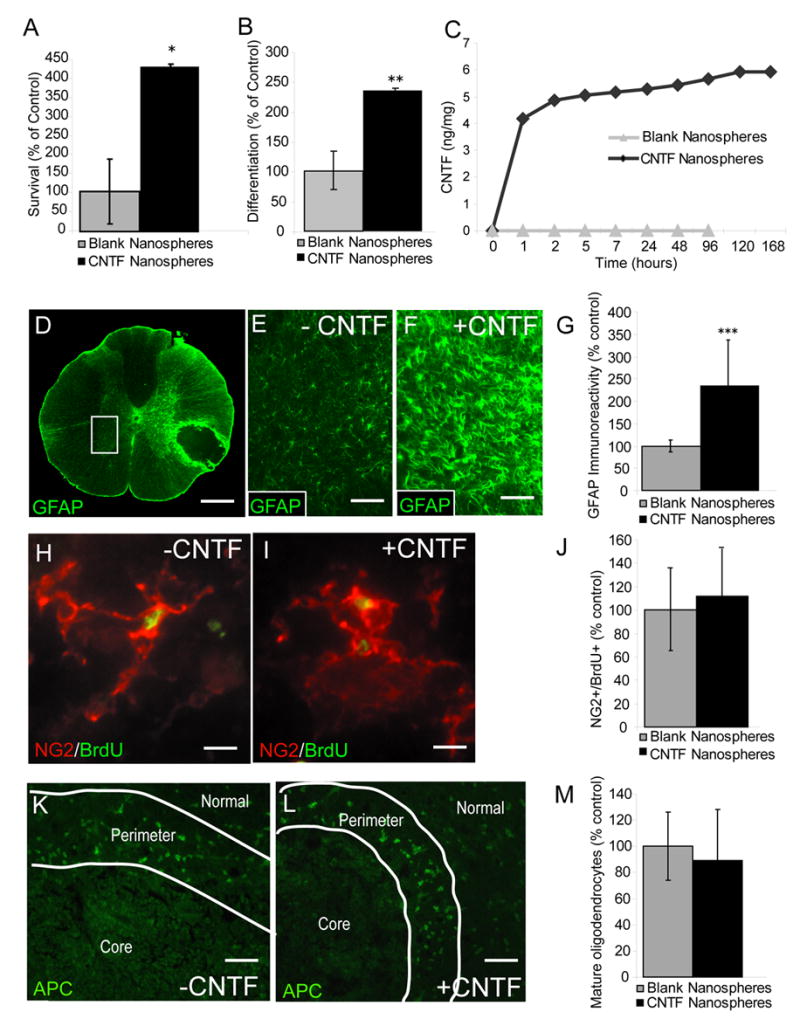
CNTF promotes the survival and differentiation of adult OPCs in vitro but not in vivo. A, The survival of newly differentiated adult OPCs was assessed using the MTT assay. Adult OPCs were differentiated for two days by withdrawal of FGF2 and PDGF-AAaa, then continued to grow in basal medium with or without CNTF (10 ng/ml) for five more days. Quantitative analysis of surviving MTT+ cells demonstrated an approximate 300% increase in survival for cells treated with CNTF relative to control (*p = 0.03, t = 4.3, df = 2). B, Adult OPCs were cultured in either basal media + 5 ng/ml FGF2 (control) or basal media + 5 ng/ml FGF2 + 10 ng/ml CNTF. FGF2 was added to both groups to minimize spontaneous OPC differentiation. As measured by expression of the more mature oligodendrocyte marker O1, CNTF treated cultures demonstrate significantly increased differentiation relative to control (**p = 0.003, t = 2.7, df = 4). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. C, CNTF-loaded nanospheres (black diamonds) release CNTF in a sustained fashion in vitro for up to 168 hours (latest time point tested) while blank nanospheres (gray triangles) release no detectable CNTF. At each time point indicated, media was completely removed and protein quantity was assessed using an ELISA kit specific for recombinant human CNTF (rhCNTF) (expressed as ng of CNTF protein per mg of CNTF-loaded nanospheres). D, GFAP immunoreactivity was assessed in the gray matter (white box) contralateral to transplanted EB lesions 7 days after nanosphere injection (6 μl of nanospheres at 25 μg/μl). Compared to blank nanospheres (E), CNTF-nanosphere (F) injection into EB lesions of the ventrolateral funiculus (VLF) dramatically increases GFAP immunoreactivity in the contralateral gray matter. The area shown in E and F corresponds to a high magnification view of the region delineated by the white box in D. G, Quantitative pixel counts of GFAP immunoreactivity 9 days after nanosphere injection demonstrates a 130% increase in the contralateral gray matter of CNTF-nanosphere treated lesions compared to blank nanospheres (*** p < 0.001, t = 2.1, df = 20). EB lesions treated with blank (H) or CNTF-loaded (I) nanospheres (6 μl of nanospheres at 25 μg/μl) 5 days after EB injection contain similar densities of NG2+/BrdU+ cells at 14 days after EB injection (J, p = 0.54, t = 0.62, df = 16). BrdU pulse labeling (100 mg/kg every twelve hours) was performed during days 2, 3, and 4 post EB injection. K-M, Quantitative analysis of APC/CC-1+ profiles in the perimeter of (K) blank and (L) CNTF-nanosphere treated lesions was performed 4 weeks after nanosphere injection (M, p = 0.45, t = 2.1, df = 18). A,B,F,I,L, The mean ± standard deviation are expressed as the percentage of control where the average density of positive profiles in blank nanosphere-injected lesions equals 100%. Independent t-tests were performed for all statistical analysis. Scale bar = 300 μm in (D); 75 μm in (E,F); 65 μm in (H,I).
