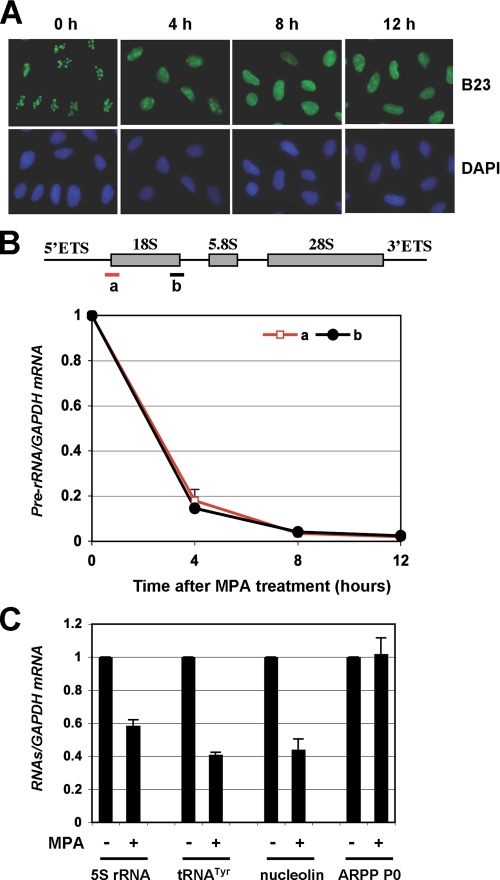
FIGURE 2.
MPA treatment induces redistribution of B23 into the nucleoplasm and inhibits pre-rRNA synthesis. A, MPA treatment induces redistribution of B23 into the nucleoplasm. U2OS cells were treated with methanol or 10 μmol/liter MPA for different time points (h). The cells were immunostained with anti-B23 (green) and anti-NS (red) as well as DAPI for DNA. B, MPA treatment inhibits pre-rRNA synthesis. U2OS cells were treated with 10 μmol/liter MPA for different time points (h). Total RNAs were prepared from cells and retrotranscribed. Real-time PCR analysis was then conducted to determine the relative expression of the pre-rRNA as normalized against GAPDH mRNA. Similar results are shown using two pairs of primers amplifying a fragment between 5′-ETS and 18S rRNA (a) and a fragment between 18S rRNA and ITS-1 (b), respectively, as indicated in the diagram illustrating the pre-rRNA gene structure in the top panel. C, effect of MPA treatment on levels for 5S rRNA, tRNATyr, nucleolin, and ARPP P0 RNAs. U2OS cells were treated with 10 μmol/liter MPA for 12 h, and total RNAs were prepared from cells and retrotranscribed. Real-time PCR analysis was then conducted to determine the relative expression of the RNAs as normalized against GAPDH mRNA.