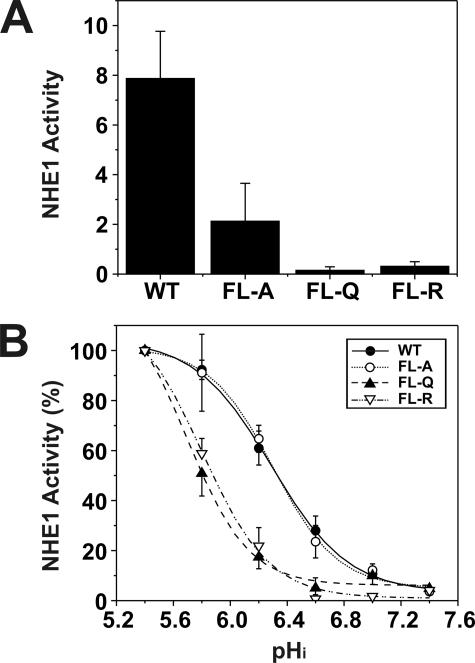
FIGURE 5.
Comparative analysis of rates of H+-activated 22Na+ influx of AP-1 cells transfected with wild-type or mutant forms of NHE1. AP-1 cells stably transfected with wild-type (WT) or mutant forms (FL-A, -Q, or -R) of NHE1HA were grown to confluence in 24-well plates. Initial rates of amiloride-inhibitable H+-activated 22Na+ influx were measured at various intracellular H+ concentrations over the range of pHi 5.4 to 7.4. The pHi was adjusted by the K+-nigericin method, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” To facilitate comparison of the effects of mutating the CHP-binding site, the rates of 22Na+ influx (pmol/min/mg total cellular protein) of wild-type and mutant forms of NHE1HA were normalized to their respective plasmalemmal (fully glycosylated) protein levels, as determined by densitometry. A, comparison of the near-maximal velocities of the various NHE1 constructs. B, percentage of the transport velocities of WT and mutant NHE1 as a function of the intracellular H+ concentration, each normalized to their respective maximal rates of uptake. Values represent the mean ± S.E. of three experiments, each performed in triplicate. Error bars smaller than the symbol are absent.