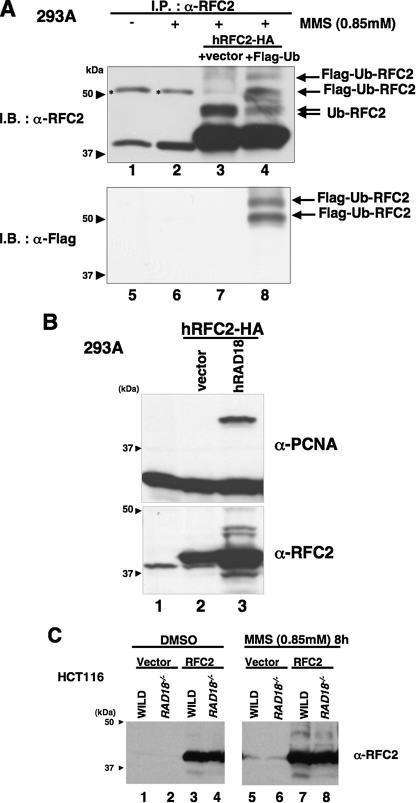
FIGURE 2.
RFC2 monoubiquitylation in response to DNA-damaging agents is RAD18-dependent. A, lysates from RFC2-HA- and FLAG-ubiquitin-co-transfected 293A cells were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. pCDNA3·RFC2-HA was co-transfected either with pCAGGS-FLAG-Ubiquitin (lanes 4 and 8) or empty vector (lanes 3 and 7) in 293A cells. The following day, cells were treated with MMS for 8 h, and then cell extracts were recovered. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-RFC2 antibody. The resulting immune complexes were recovered using protein A/G-agarose and detected by immunoblotting with anti-RFC2 antibody (lanes 1–4) or anti-FLAG antibody (lanes 5–8). Asterisks show nonspecific bands. B, Western blot of lysates from 293A cells overexpressing hRAD18. pCDNA3·RFC2-HA was co-transfected either with pCAGGS·hRAD18 (lane 3) or empty vector (lane 2) in 293A cells. Chromatin fractions were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-RFC2 (lower panel) or anti-PCNA (upper panel). The arrowheads indicate the position of molecular mass markers (kDa). C, Western blot of lysates from HCT116 cells (WILD) or RAD18-deficient HCT116 cells (RAD18-/-). HCT116 cells transfected either with empty vector or pCAGGS·hRFC2 were treated with 0.85 mm MMS for 8 h. Chromatin fractions from the resulting cells were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-RFC2 antibody. The arrowheads indicate the position of molecular mass markers (kDa). I.P., immunoprecipitate; I.B., immunoblot; DMSO, Me2SO; Ub, ubiquitin.