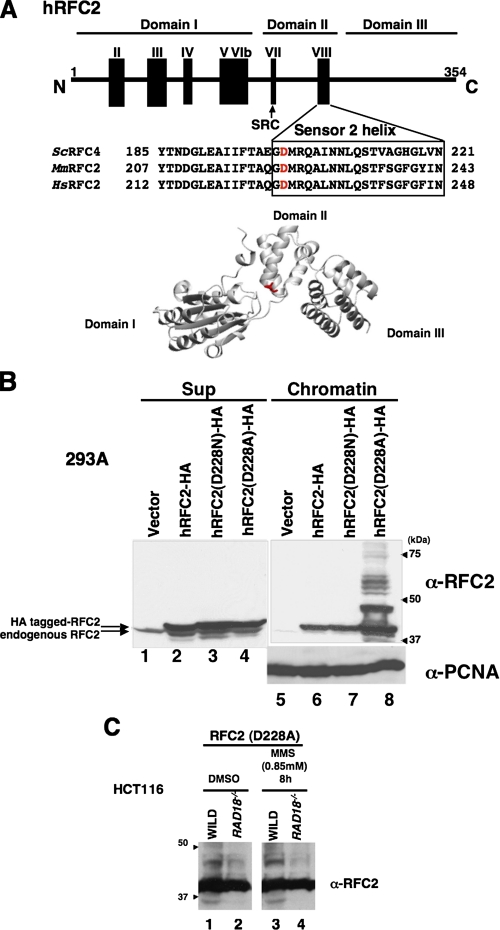
FIGURE 3.
DNA damage-independent monoubiquitylation of hRFC2 D228A. A, schematic diagram and tertiary model of human (Hs) RFC2 showing the location of Asp-228 and the sequences of the surrounding regions. Corresponding sequences for S. cerevisiae (Sc) RFC2(p40) and mouse (Mm) RFC2 homologues are also shown. The conserved Sensor 2 helix is represented by a box, and the location of the conserved SRC motif is indicated by an arrow. Asp-228 of hRFC2, shown in red, corresponds to S. cerevisiae Asp-201, which shows synthetic lethality with mutation in Rpa-1(rfa1-Y29H). There are seven conserved RFC boxes numbered consecutively from the N terminus to C terminus. B, 293A cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding wild-type (lanes 2 and 6), D228N (lanes 3 and 7), or D228A (lanes 4 and 8) forms of hRFC2-HA. 24 h after transfection cells were harvested and separated into chromatin (lanes 5–8) and soluble fractions (lanes 1–4) and then immunoblotted with anti-RFC2 or anti-PCNA antibody. The arrowheads indicate the position of molecular mass markers (kDa). C, Western blot of lysates from HCT116 cells (WILD) or RAD18-deficient HCT116 cells (RAD18-/-). HCT116 cells transfected with pCAGGS·hRFC2(Asp-228) were treated with 0.85 mm MMS for 8 h. Chromatin fractions from the resulting cells were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-RFC2 antibody. The arrowheads indicate the position of molecular mass markers (kDa). DMSO, Me2SO.