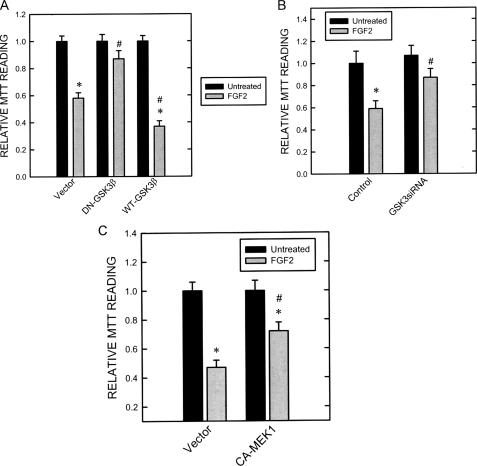
FIGURE 7.
Effect of dominant negative (DN), wild-type (WT) GSK3β, GSK3β siRNA, and CA-MEK1 on FGF2-induced cell death. A, SK-N-MC cells stably expressing dominant negative or wild-type GSK3β constructs were established as described under “Experimental Procedures.” These cells were treated with FGF2 (0 or 10 ng/ml) for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each data point (±S.E.; bar) is the mean of three experiments. Asterisk, FGF2-induced death; denotes significant difference from untreated controls (black bar versus gray bar within group). #, DN-GSK3β-mediated protection; denotes significant difference from FGF2-exposed cultures in the empty vector-treated group (gray bar in DN-GSK3β-treated group versus gray bar in empty vector-treated group). B, after transfection with GSK3β siRNA or control siRNA for 48 h, cells were treated with FGF2 (0 or 10 ng/ml) for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT. C, after transfection with CA-MEK1 or empty vector for 48 h, cells were treated with FGF2 (0 or 10 ng/ml) for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT. Each data point (±S.E.; bar)is the mean of three experiments. Asterisk, FGF2-induced cell death (black bar versus gray bar within group). #, GSK3β siRNA or CA-MEK1 mediate protection (gray bars in GSK3β siRNA- or CA-MEK1-treated group versus gray bars in empty vector-treated group).