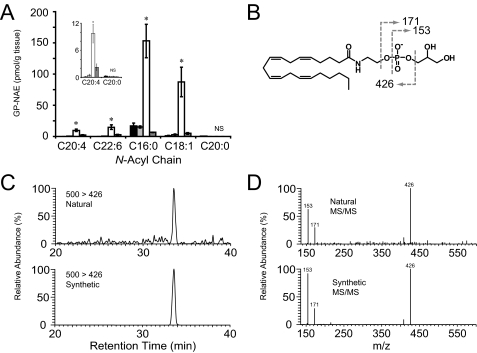
FIGURE 3.
Ex vivo accumulation of GP-NAEs in brain tissue via an MAFP-sensitive and EDTA-dependent enzymatic pathway. A, GP-NAE levels in brain tissue homogenized in buffer (50 mm Tris, pH 8.0) alone (black and light gray bars), buffer with 10 mm EDTA (open bars) or 10 mm EDTA and 20 μm MAFP (dark gray bars). Homogenates were incubated for 0 h (black bars) or 4 h (all other bars) and then subjected to organic extraction and LC-MS/MS analysis. The inset shows a magnification of low abundance GP-NAEs. Student's t test compared EDTA-treated to samples treated with EDTA and MAFP; asterisk indicates p < 0.05; NS, not significant (n = 4 per group). B, fragmentation of N-arachidonoyl-GP-NAE produces a diagnostic NAE-phosphate fragment (m/z 426) and two fragments corresponding to glycerol 3-phosphate and its dehydrate at 171 and 153, respectively. Representative chromatographs (C) and tandem MS fragmentation (D) are shown for synthetic GP-NArE and natural GP-NArE, which accumulates in the presence of EDTA.