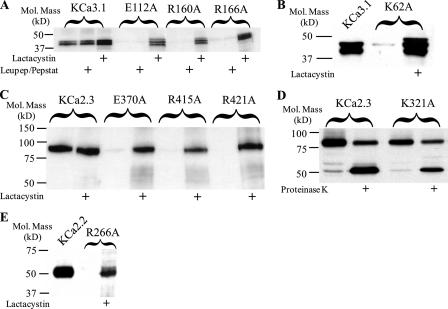
FIGURE 2.
Immunoblots demonstrating that degradation of S3 and S4 charged amino acid mutations is prevented by lactacystin. A, degradation of E112A, R160A, and R166A KCa3.1 is prevented by the proteasome inhibitor, lactacystin (10 μm), whereas the combination of lysosomal inhibitors, leupeptin (15 μm) and pepstatin (15 μm), had no effect on protein expression. Note that wild type KCa3.1 protein expression is also increased by lactacystin indicating some wild type channel is targeted to the proteasome. B, degradation of the S2 mutation K62A is prevented by lactacystin. C, degradation of E370A, R415A, and R421A KCa2.3 is prevented by the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin, whereas wild type KCa2.3 expression is unaffected. D, S2 mutation K321A in KCa2.3 is expressed at a similar level as wild type KCa2.3 (compare 1st and 3rd lanes). Digestion with proteinase K results in a lower molecular weight band in both wild type and K321A KCa2.3 (2nd and 4th lanes), indicative of these channels being expressed at the plasma membrane. E, degradation of the S4 mutation R266A in KCa2.2 is prevented by lactacystin. A, B, and E, 20 μg of total protein was loaded per lane; C and D, 10 μg of total protein was loaded per lane.