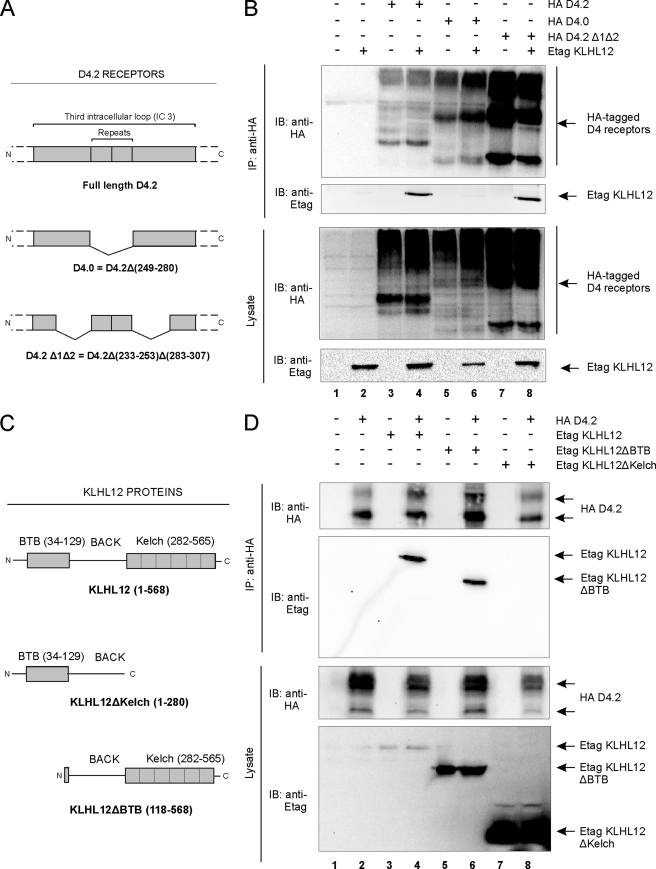
FIGURE 3.
Domain mapping of the D4 receptor-KLHL12 interaction. A, schematic illustration of the HA D4.2 receptor protein and deletion mutants used in this study. B, HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with the plasmids expressing Etag KLHL12 (5.5 μg) together with the HA D4.2 receptors (5.5 μg) depicted in A, in the indicated combinations. 48 h post-transfection, cells were lysed, and 5% of the lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. The presence of all three HA D4 receptors and Etag KLHL12 was revealed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA and anti-Etag, respectively. The rest of the lysates was subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA. The KLHL12-D4 receptor association was examined by immunoblotting with anti-Etag, whereas the immunoprecipitation was confirmed by subsequent immunoblotting with anti-HA. C, schematic illustration of the wild type KLHL12 protein and deletion mutants used in this study. The depicted sequences were fused to an N-terminal Etag. D, HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing the HA D4.2 receptor (5.5 μg), Etag KLHL12 (5.5 μg), and the deletion mutants Etag KLHL12ΔBTB (5.5 μg) and Etag KLHL12ΔKelch (5.5 μg). Co-immunoprecipitation was examined by subsequent immunoprecipitation-immunoblot, as described in B. The expression of the HA D4.2 receptor and the Etag KLHL12 full-length and deletion mutant proteins in lysates was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-Etag, respectively (bottom).