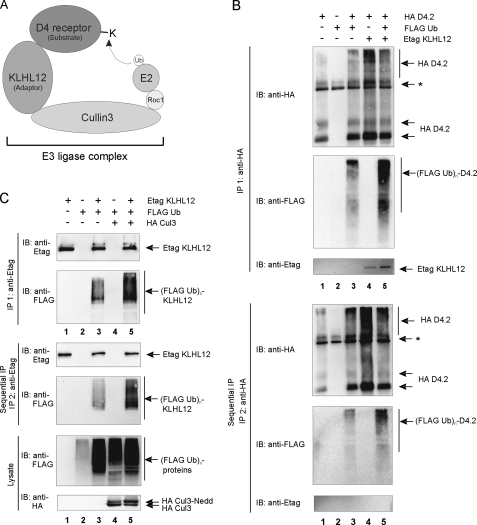
FIGURE 6.
Ubiquitination of the D4 receptor and KLHL12 in eukaryotic cells. A, schematic illustration of the D4 receptor-KLHL12-Cul3 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. E2 represents the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme; Roc1 (Rbx1 and Hrt1) is the RING finger factor; Cul3 serves as the scaffold protein for both Roc1 and KLHL12. The D4 receptor is targeted to the E3 ligase by the adaptor protein KLHL12 and functions as a substrate for subsequent ubiquitination by E2. B, HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding the HA D4.2 receptor (4 μg), FLAG-tagged ubiquitin (FLAG Ub; 4 μg) and Etag KLHL12 (4 μg) as indicated. 48 h post-transfection, cells were lysed. The lysates were subjected to a first immunoprecipitation (IP 1) with anti-HA. Bound proteins were eluted from the washed immunoprecipitates; a quarter of the eluate was subjected to SDS-PAGE and subsequent immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA to confirm immunoprecipitation of the HA D4.2 receptor and anti-FLAG antibody to detect ubiquitination (top; (FLAG Ub)n-D4.2). Detection of Etag KLHL12 in the immunoprecipitates was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-Etag. The rest of the eluate was diluted with lysis buffer and subjected to a second immunoprecipitation round (IP 2) with anti-HA. Bound receptor was eluted from the washed immunoprecipitates. The eluate was again subjected to SDS-PAGE and subsequent immunoblotting with anti-HA to confirm the second immunoprecipitation of D4.2 receptor and anti-FLAG to detect specific ubiquitination of the D4.2 receptor (bottom). The exclusion of KLHL12 from the second immunoprecipitates was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-Etag. *, the signal is a combination of IgG, a nonspecific signal from the anti-HA antibody, and a D4-specific signal in lanes 1, 3, 4, and 5. C, HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing Etag KLHL12 (4 μg), FLAG Ub (4 μg), and HA Cul3 (4 μg). 48 h post-transfection, cells were lysed. A small fraction of each lysate was subjected to SDS-PAGE to confirm the expression of FLAG Ub and HA Cul3 by immunodetection with anti-FLAG and anti-HA, respectively. The rest of the lysates were subjected to a first immunoprecipitation using anti-Etag. Bound proteins were eluted from the beads; 20% of the eluate was subjected to SDS-PAGE and subsequent immunoblotting with anti-Etag to confirm immunoprecipitation of Etag KLHL12 and with anti-FLAG to detect ubiquitinated Etag KLHL12 (top; (FLAG Ub)n-KLHL12). The rest of the eluate was diluted with lysis buffer and subjected to a second immunoprecipitation round with anti-Etag. Bound Etag KLHL12 was eluted from the washed immunoprecipitates and again subjected to SDS-PAGE. The second immunoprecipitation of Etag KLHL12 was confirmed by subsequent immunoblotting with anti-Etag, whereas specific ubiquitination of Etag KLHL12 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG.