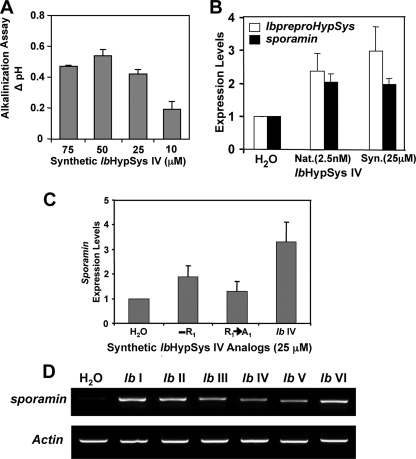
FIGURE 6.
Biological activities of native and synthetic IbHypSys peptides. A, the change in pH of the medium of suspension cultured tomato cells in response to increasing concentrations of IbHypSys IV, when compared with H20 controls. The pH was recorded 30 min after adding 10 μl of the peptide solution to 1 ml of suspension cultured tomato cells. B, expression of IbpreproHypSys and sporamin in excised sweet potato leaves supplied for 2 h with 2.5 nm native (Nat.) IbHypSys or 25 μm synthetic (Syn.) IbHypSys IV, assayed by RT-PCR. The expression of actin was used as an internal control. Leaves supplied with water alone (H2O) were assayed as a reference. The data shown are from a representative experiment from three replications. C, sporamin expression levels induced in sweet potato leaves fed synthetic IbHypSysIV analogs. IbHypSysIV and synthetic analogs were dissolved in distilled H2Oata concentration of 25 μm and supplied to excised leaves for 2 h as described under “Experimental Procedures.” IbHypSysIV minus the N-terminal arginine (-R1), IbHypSysIV with alanine substituted for arginine at the amino terminus (R1→A1) The expression levels of sporamin were estimated using RT-PCR with actin as an internal control. Data represent three replications. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. D, the induction of sporamin by synthetic peptides (see “Experimental Procedures”). Excised young sweet potato leaves were supplied with 25 μm of each synthetic peptide or water for 2 h, and the expression levels of sporamin were estimated using RT-PCR, with actin as an internal control.