Fig. 2.
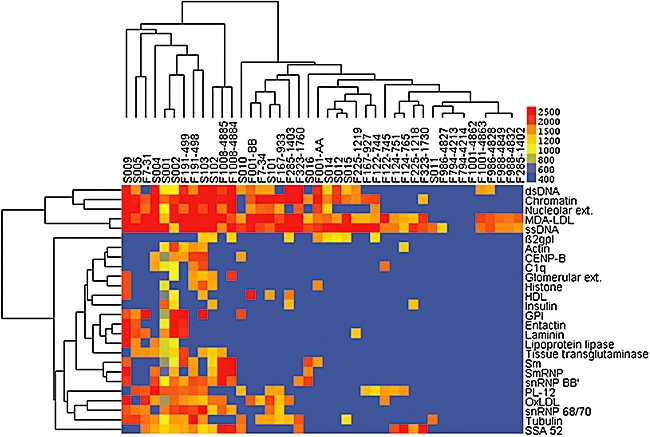
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) autoantibody profiling of sera samples from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Hierarchical cluster analysis results were performed shown for IgM reactivity with the panel of 14 twin sets and 14 unrelated SLE patients. Results are depicted after removal of antigens for which five or fewer individuals were reactive, which yielded a smaller panel of 26 antigens. Twins are identified by shared ‘F’ naming, while unrelated SLE patients are identified by ‘S’. Based on hierarchical cluster analyses, related IgM autoantibody profiles were identified for monozygotic (MZ) twins (F122, F124, F191 and F1008) and for two dizygotic (DZ) twins (F988 and F1001). Lupus-discordant twin sets were F001, F122, F988 and F1001. Control array studies demonstrated a trend in SLE patients (n = 10) towards higher IgM autoantibodies than in healthy controls (n = 10) to: oxidated low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) (mean ± standard deviation) 5049·6 ± 3575 versus 2239 ± 2840; malondialdehyde (MDA)-LDL, 4607 ± 3406 versus 1736 ± 1379; phosphorylcholine-albumin, 16760 ± 14501 versus 12936 ± 10286; MDA-albumin, 3289 ± 3338 versus 904 ± 942.
