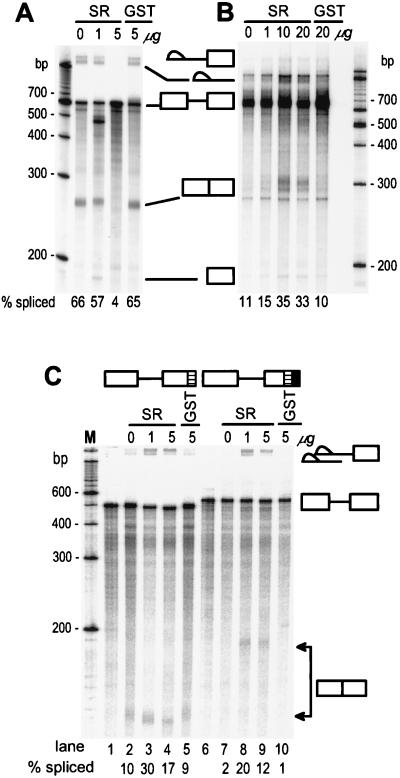
Figure 5.
Restoration of ESS-suppressed splicing of BPV-1 late and HIV-1 tat/rev pre-mRNA by addition of excess exogenous SR proteins. BPV-1 late pre-mRNAs A (no ESS) and B (ESS +) in Fig. 3D and HIV-1 tat/rev pre-mRNA were used in this study. All of the pre-mRNAs were prepared by in vitro transcription and labeled by incorporation of 32P-rGTP (13). Different concentrations of purified HeLa SR proteins or recombinant glutathione S-transferase (GST) protein were added to each standard splicing reaction. Addition of 10 μg of purified SR proteins approximately doubles the amount of SR proteins in the splicing reaction. The spliced products of each pre-mRNA were resolved by electrophoresis on an 8% polyacrylamide-8 M urea gel and shown in A (BPV-1 late pre-mRNA A in Fig. 3D), B (BPV-1 late pre-mRNA B in Fig. 3D), and C (HIV-1 tat/rev pre-mRNA). The structures of HIV-1 tat/rev pre-mRNAs are diagramed at the top of C with the HIV-1 tat/rev ESE indicated as a hatched box and the BPV-1 ESS as a filled box. Lanes 1–5 are the ESS (−) HIV-1 tat/rev pre-mRNA and lanes 6–10 are the ESS (+) HIV-1 tat/rev pre-mRNA. Lanes 1 and 6 are the unspliced pre-mRNA controls. The splicing efficiency of each pre-mRNA was calculated based on the gel profile in each panel and shown at the bottom of each splicing gel.