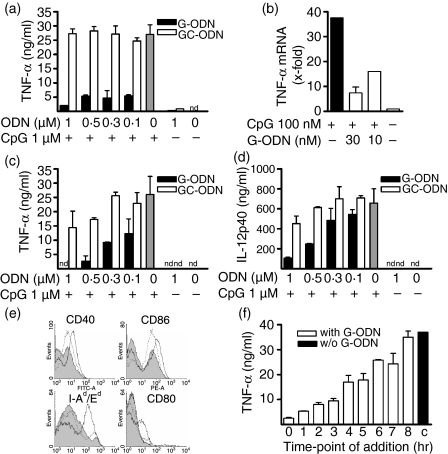
Figure 1.
Guanosine-rich oligodeoxynucleotide (G-ODN) inhibits CpG-induced activation of macrophages and dendritic cells. (a) RAW264.7 cells were incubated overnight with 1 µm CpG-ODN in the presence of the indicated concentrations of G-ODN or GC-ODN, respectively. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was measured in the supernatant. (b) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with 100 nm CpG-ODN in the presence of the indicated concentrations of G-ODN for 4 hr; mRNA was extracted and the relative expression of TNF-α was quantified by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). (c,d) Bone-marrow dendritic cells (BMDC) were stimulated overnight with 1 µm CpG-ODN in the presence of G-ODN or GC-ODN. TNF-α and interleukin (IL)-12p40 were determined in the supernatant. (e) BMDC were left untreated (solid grey) or were stimulated overnight with 1 µm CpG-ODN (thick line) and stained for surface expression of the indicated marker. Additionally, cells were stimulated with CpG-ODN in the presence of 0·3 µm G-ODN (dotted line). (f) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with 1 µm CpG-ODN. At the indicated time, 0·3 µm G-ODN was added. Sixteen hours after stimulation, TNF-α was determined in the supernatant (mean plus standard deviation, one representative experiment out of at least three independent experiments). nd, not determined.