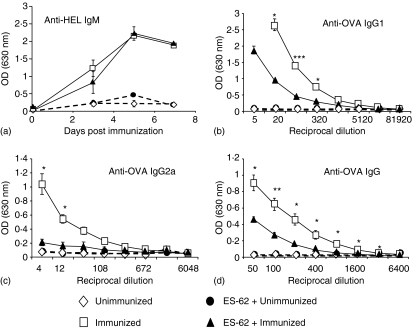
Figure 3.
Effects of ES-62 on the anti-HEL IgM response and of antigen-specific B cells on the ability of ES-62 to modulate the production of OVA-specific IgG1 and IgG2a in vivo. Non-transgenic BALB/c recipient control and ES-62-treated mice were injected with 2·5 × 106 CD4+ KJ1.26+ T cells and B220+ HEL+ B cells. Twenty-four hr later, these mice were immunized s. c with 130 µg OVA–HEL in CFA. In (a), serum (1/200 dilution) was prepared at 3, 5 and 7 days after immunization and HEL-specific IgMa was assessed by ELISA. Each time point represents the mean OD at 1/200 dilution for three mice per group ± SEM. Data are representative of two independent experiments. In (b–d), serum was collected at 10 days after immunization and OVA-specific IgG1 (b), IgG2a (c) and IgG (d) were assessed by ELISA. Data are presented as the mean of three mice per group ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments. ***P < 0·005, **P < 0·01, *P < 0·05.