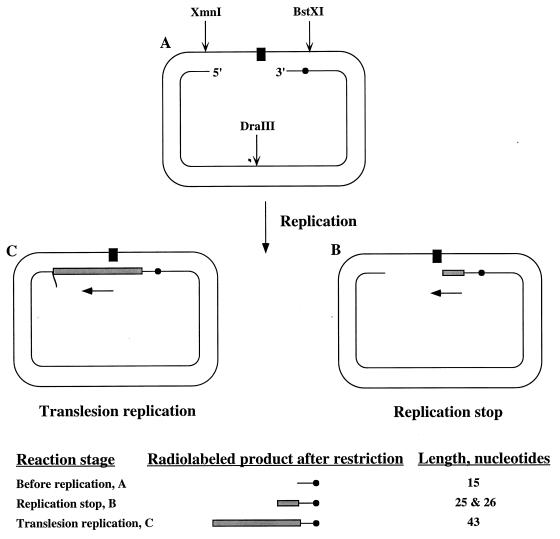
Figure 1.
The translesion replication assay. The substrate for the translesion replication was a gapped plasmid, carrying a site-specific synthetic abasic site, and an internal radiolabeled phosphate. After replication, the DNA was restricted with restriction nucleases BstXI and XmnI, and the products were fractionated by urea-PAGE. Visualization and quantification was done by phosphorimaging. The bottom panel shows the types of replication products obtained. The unextended DNA is a 15-mer whereas replication arrest before or opposite the lesion forms a 25-mer or 26-mer, respectively. Translesion replication forms products longer than 26-mer: A pause of the polymerase at the end of the gap yields a 37-mer whereas further elongation, which requires strand displacement, forms products longer than 37-mer. Replication past the XmnI site will be indicated by products 43 nucleotides long, dictated by the XmnI cleavage site. If the polymerase skips the lesion, producing a −1 deletion, a 42-nt product is expected. Black rectangle, abasic site analog; black circle, radiolabeled phosphate; gray bar, newly synthesized DNA.