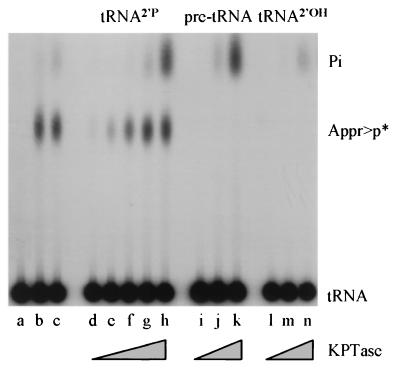
Figure 2.
E. coli KptA protein transfers the 2′-phosphate from the substrate ligated tRNA. Different 32P-labeled derivatives of the substrate were tested as the source of the transferred phosphate, with 1 mM NAD and 5-fold serial dilutions of KptA protein, starting from 125 units of activity. After incubation, 0.1 unit of calf intestinal phosphatase was added to each tube, followed by a further 15-min incubation, to convert contaminating nuclease products (but not Appr>p) to Pi, and samples were applied to TLC plates. Lanes d–h, ligated tRNAPHE with a labeled 2′-phosphate (the standard substrate); i–k, labeled pre-tRNA as substrate; and l–n, mature tRNA (previously dephosphorylated with yeast Tpt1 protein). Lanes a–c, controls with ligated tRNA substrate and NAD: a, buffer control, followed by CIP buffer; b, Tpt1p, followed by CIP buffer; c, Tpt1p, followed by CIP.