Fig. 1.
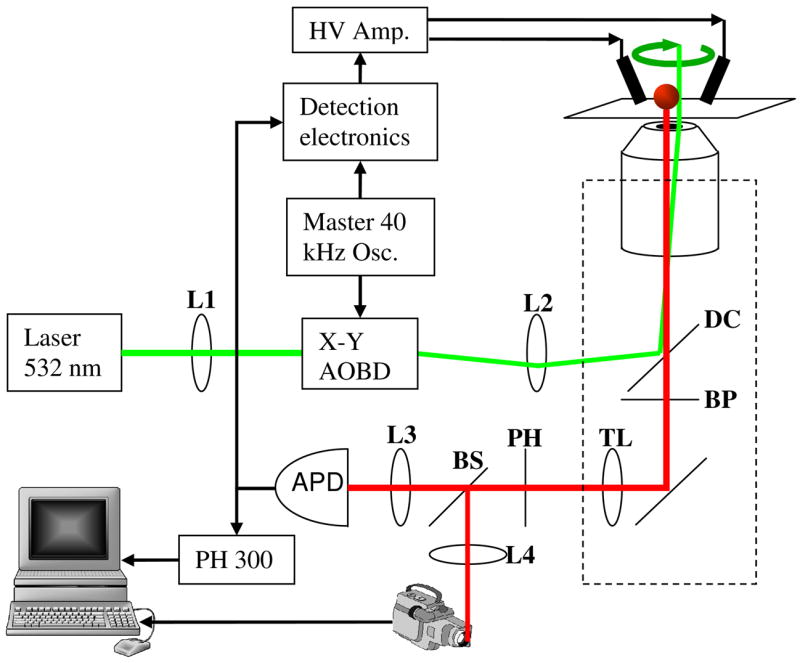
Schematic of the hardware-feedback ABEL trap. A two-dimensional acousto-optic beam deflector (AOBD) deflects a laser beam in a small circle at 40 kHz. The excitation light reflects of dichroic mirror DC and illuminates a particle in the trap. A bandpass filter BP blocks scattered excitation light while passing fluorescence. The tube lens TL focuses the fluorescence onto a pinhole PH, and the fluorescence photons are then detected by an avalanche photodiode (APD). Phase-sensitive detection of individual photons provides a sensitive indicator of the offset between the location of the particle and the center of the trap. A time-correlated single-photon counting module (PH 300) records the arrival time of each photon, and a beamsplitter BS diverts a small fraction of the fluorescence light toward a camera.
