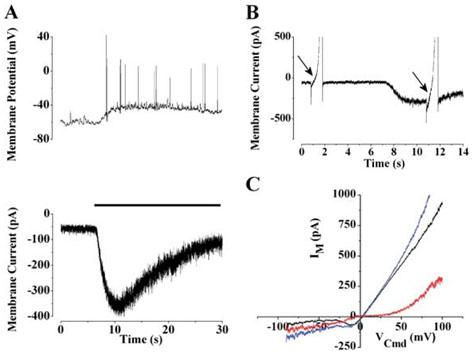
FIG. 5.
Current–voltage relationship of the light-activated current. (A) The lower panel shows the light response (black bar; irradiance 5.8×10−5W/cm2) of an SCN-projecting RGC recorded in voltage-clamp mode. To illustrate the similar time courses, a light response recorded in current-clamp mode is shown in the upper panel. (B)To determine the voltage dependence of the light-activated current, voltage ramps (−100 to +100 mVover 2 s) were applied before and during illumination. (C) The light-activated current (red) was determined by subtracting currents elicited by the voltage ramp before (black) and during (blue) illumination.