FIG. 1.
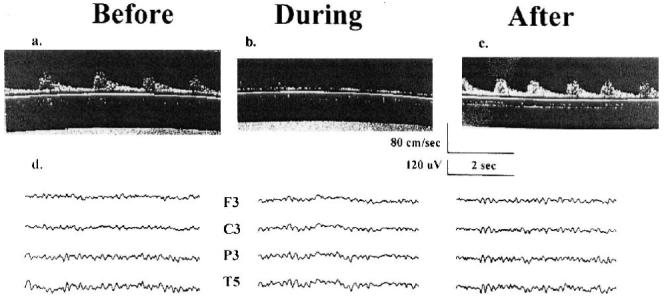
Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography and electroencephalogram. A, B and C are three transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasonography records from the patient reported in Case 1 with the TCD probe placed over the left temporal bone and insonated on the middle cerebral artery. “Before,” “during,” and “after” refer to three different records of cerebral blood flow (CBF) velocity taken at different times during surgery: before the carotid artery is clamped, while the carotid artery is clamped, and after the clamp has been removed. The scales for time in seconds and CBF velocity in cm/sec are shown below C. D shows three electroencephalographic (EEG) records taken at the three times described above. Ten electrodes are applied using an Electro-Cap (Electro-Cap International Inc., Eaton, OH). The electrodes are arranged in a referential montage using the International 10-20 positioning system with four over each hemisphere (Frontal [F], Central [C], Parietal [P], and Temporal [T]). The “reference” electrode placed centrally at Cz (“Z” refers to midline), and a “ground” electrode at Fz. Only the EEG traces for the left hemisphere are shown. The scales for time in seconds and EEG amplitude in μV are shown below C.
