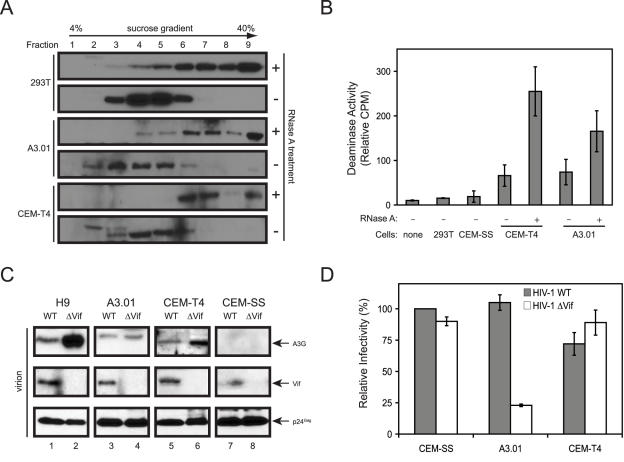
Figure 2. Characterization of A3G in CEM-T4 cells.
(A) Isolation of A3G protein complexes. Cytosolic fractions were prepared from CEM-T4, A3.01, and 293T cells transfected with human A3G expression vector. These lysates were treated or untreated with RNase A and then loaded on the top of a 4% to 40% sucrose gradient. After centrifugation at 200,000g for 4 h, 9 fractions were collected, and A3G expression was determined by Western blotting. (B) A3G deaminase activity. Cell lysates were prepared from indicated cell lines with or without RNase A treatment and then subjected to scintillation proximity-based cytidine deaminase assay. Error bars represent standard deviations in 3 independent experiments. (C) Production of HIV-1 from human T cell lines. H9, A3.01, CEM-SS, and CEM-T4 cells were infected with wild-type or vif-defective HIV-1 carrying a neomycin-resistant gene, and stable cell lines were generated by G418 selection. Viruses were then collected from these cultures, and virion-associated proteins were determined by Western blotting. (D) Viral infectivity assay. Viruses produced from the stable cell lines were collected and used to infect TZM-bI cells. Viral infectivity was determined and normalized to viral input and expressed as relative values to the wild-type virus infectivity from CEM-SS cells. The values for wild-type and vif-deficient virus infectivity are 100 and 90 from CEM-SS, 105 and 23 from A3.01 cells, and 72 and 89 from CEM-T4 cells. Error bars represent standard deviations in 3 independent experiments.