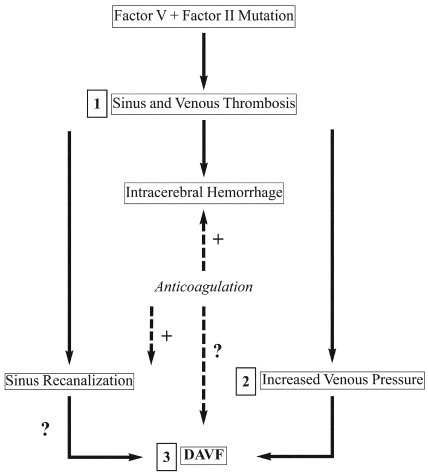
Figure 2.
The flowchart shows the mechanism proposed to underlie the development of the patient's complex clinical picture. The genetic process begins with the mutation that caused the thrombosis and hemorrhage (1). Increased venous pressure (2) leads to the DAVF (3). Treatment with anticoagulation is a dilemma because of its beneficial effects on thromboembolic events and its adverse effects on hemorrhage. The dotted lines indicate the possible positive effects on recanalization of the thrombosed sinus but the increased risk of hemorrhage and development of the DAVF. (With permission from Barrow Neurological Institute.)