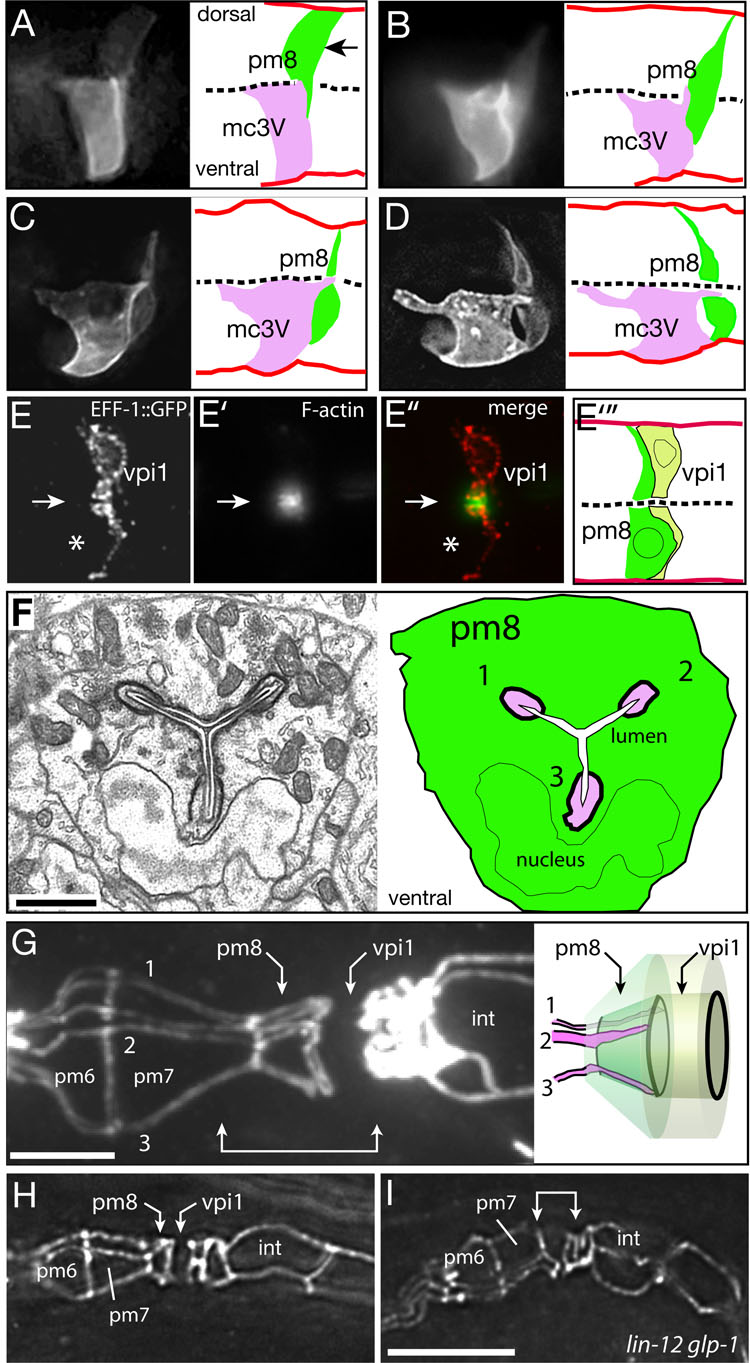
Figure 4. Ventral migration and lumen formation in pm8 and vpi1.
(A–D) ref-1::GFP-PM expression in pm8 and the group 3 marginal cell mc3V in successively older embryos. Images are optical sections through the midline of the cyst; a complete image series corresponding to panel D is shown in Movie S4. (E–E”) vpi1 expressing eff-1::EFF-1::GFP and stained with phalloidin to visualize F-actin at the midline (arrow); note relative absence of actin in pm8 (asterisk indicates position of pm8 nucleus). Panel E”’ is a diagram of vpi1 with the approximate position of the pm8 cell body included for reference (see Fig S3D). (F) Electron micrograph and diagram of a cross section through pm8 in an embryo near hatching. The three marginal cell fingers (numbered 1–3) are evident in the Y-shaped lumenal channel (white) of pm8. (G) Apical junctions in a wild-type, third stage (L3) larva; cells in the pharynx and valve do not divide during larval development, but increase in size and allow better visualization of apical junctions. Apical surfaces of cell like pm7 resemble broad triangles, while the group 3 marginal cells (numbered 1–3) have long, thin apical surfaces (see also Movie S1). Note how fingers from the marginal cells extend through the apical surface of pm8. The region indicated by the double-headed arrow is diagrammed to show a superposition of the pm8 and vpi1 cell bodies on their apical surfaces; apical junctions are drawn in black. (H, I) Same region as in panel F in wild-type (H) and lin-12 glp-1 mutant (I) embryos near hatching. Bars = 1 µm (F), 5 µm (F–H).