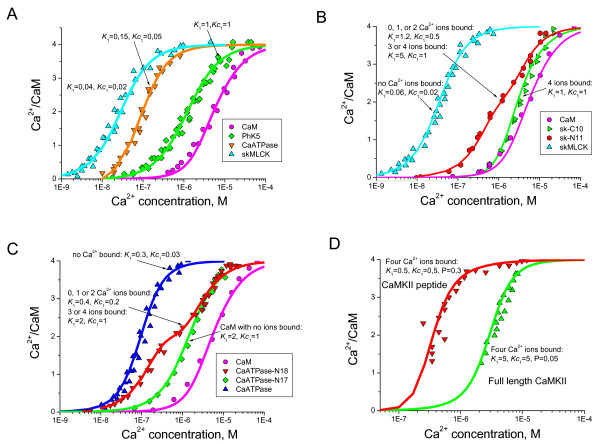
Figure 7.
Ca2+-dependent interaction of CaM with target protein peptides. The data from [33] shows Ca2+ binding to CaM in the presence of peptides derived from phosphorylase kinase (PhK5), erythrocyte Ca2+ CaATPase, skeletal Myosin Light Chain Kinase (skMLCK) (A). (B) and (C) show the Ca2+ binding to CaM in the presence of parts of skMLCK and CaATPase peptides, respectively [33]. Interaction data for Ca2+-CaM complexes in the presence and absence of protein kinase II (CaMPKII) reveal parameters of complex formation reaction [49]. The solid line in each case shows the model prediction for Ca2+-CaM binding. K1 is macroscopic Ca2+ dissociation constant, Kc1 is the cooperatively affected dissociation constants. Arrows indicate the number of Ca2+ ions bound to CaM required to create a complex with a target molecule peptide.