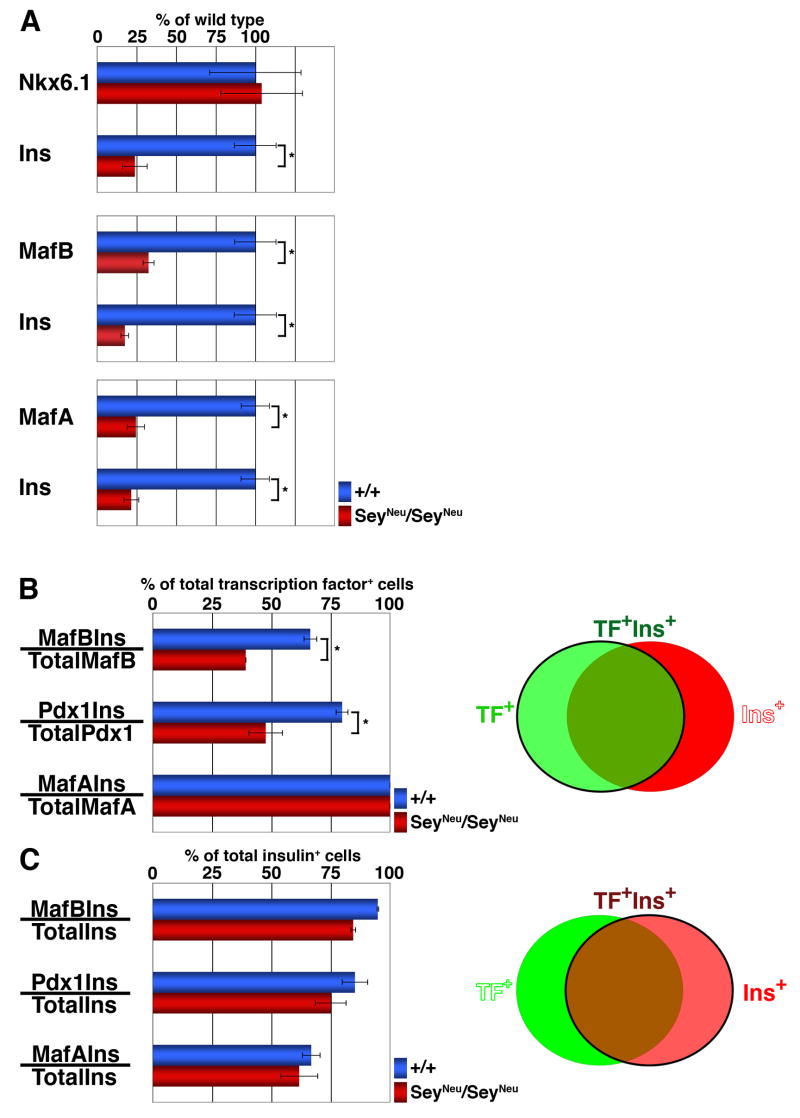
Figure 2. Pax6-deficiency reduces the proportion of MafB+ and PDX-1+ cells that express insulin.
Quantification of immunostained E15.5 embryonic pancreatic sections from wild type and SeyNeu/SeyNeu embryos (n = 6 each). (A) Total number of Nkx6.1+, MafB+ and MafA+ cells in wild type and SeyNeu/SeyNeu embryonic pancreas were determined along with the number of insulin+ cells in the same sections. In SeyNeu/SeyNeu embryonic pancreas, the numbers of MafB+, MafA+ and insulin+ cells were significantly reduced (p = 0.03, 0.01 and 0.01 respectively), while the number of Nkx6.1+ cells remained unchanged (p = 0.46). (B) The ability of transcription factor expressing cells to express insulin was determined by quantifying the proportion of transcription factor+ insulin+ cells per total number of transcription factor+ cells, as represented by cells in green circle in adjacent Venn diagram. Proportions of MafB+Ins+ cells / total MafB+ cells and PDX-1+Ins+ cells / total PDX-1+ cells in SeyNeu/SeyNeu pancreas were significantly less than the wild-type (p = 0.005 and 0.01 respectively), while all of the MafA+ cells express insulin. (C) To determine the ability of insulin+ cells to undergo further maturation in the absence of Pax6 function, the proportion of insulin+ cells expressing these transcription factors was quantified, as represented by cells in red circle in adjacent Venn diagram. The proportion of MafB+ Ins+, PDX-1+Ins+ and MafA+Ins+ cells to the total Ins+ cells was not significantly different between wild type and SeyNeu/SeyNeu mice.