Abstract
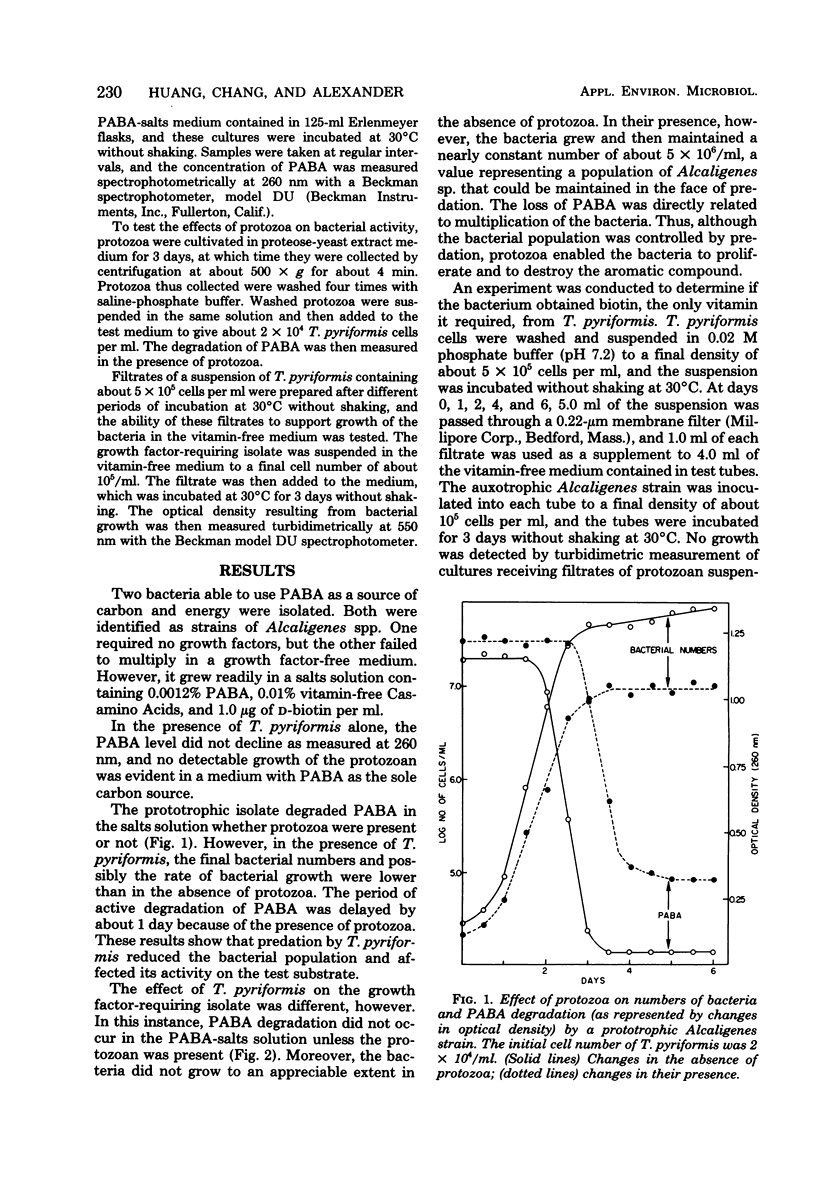
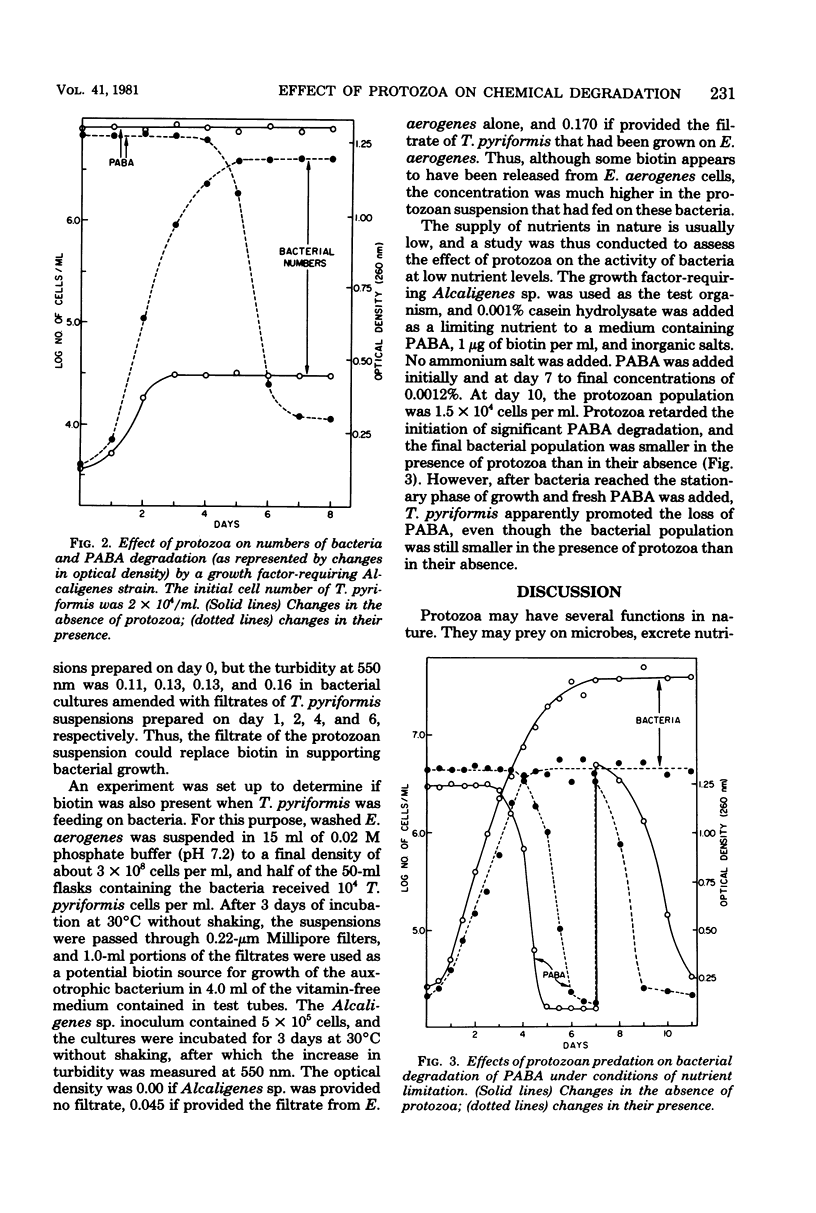
Prototrophic and growth factor-requiring strains of Alcaligenes spp. were used to study the effect of a protozoan, Tetrahymena pyriformis, on the degradation of p-aminobenzoate. The protozoan inhibited activity of the prototrophic bacterium by reducing its population size. For the growth factor-requiring strain of Alcaligenes, T. pyriformis provided the required growth factors so that the predator permitted the bacteria to grow and to continue p-aminobenzoate degradation. T. pyriformis inhibited bacterial activity when the amino acid supply was in excess, but activity of the auxotrophic strain of Alcaligenes was stimulated by the protozoan when the amino acid supply was limiting, although the bacterial population size was reduced by the protozoan.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buechler D. G., Dillon R. D. Phosphorus regeneration in fresh-water paramecia. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):339–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danso S. K., Keya S. O., Alexander M. Protozoa and the decline of Rhizobium populations added to soil. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jun;21(6):884–895. doi: 10.1139/m75-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habte M., Alexander M. Protozoa as agents responsible for the decline of Xanthomonas campestris in soil. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):159–164. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.159-164.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


