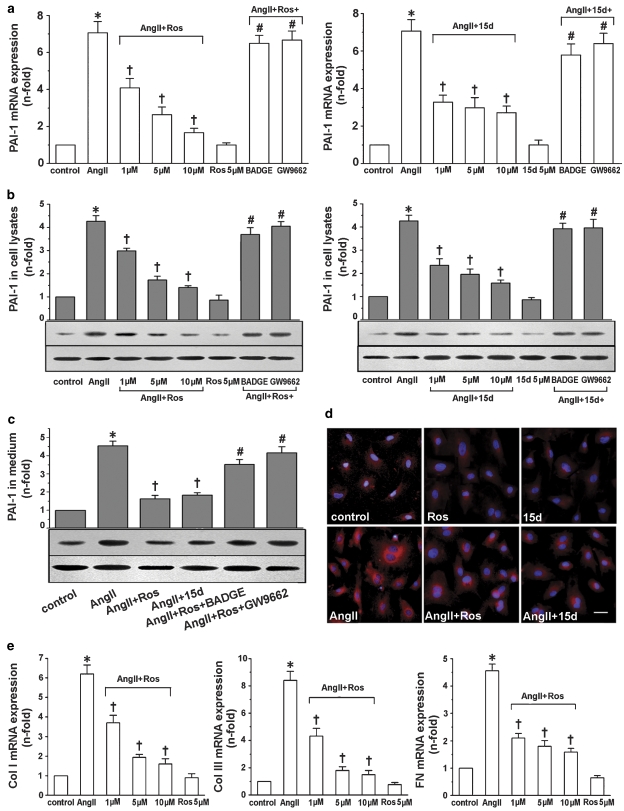
Figure 2.
Rosiglitazone and 15d-PGJ2 inhibited PAI-1, collagen I (Col I), collagen III (Col III) and fibronectin (FN) expression in Ang II-stimulated cardiac fibroblasts. Cells were pretreated with or without GW9662 (3 μM) or BADGE (1 μM) for 30 min prior to the addition of rosiglitazone (Ros; 1, 5 and 10 μM) or 15d-PGJ2 (15d; 1, 5 and 10 μM). Ang II (0.1 μM) was then added for 24 h. (a) Real-time RT-PCR revealed that rosiglitazone (left panel) and 15d-PGJ2 (right panel) inhibited Ang II-induced PAI-1 mRNA expression in a PPAR-γ-dependent manner. Western blots showed that rosiglitazone and 15d-PGJ2 inhibited Ang II-induced PAI-1 protein synthesis (b) and secretion (c) in a PPAR-γ-dependent manner. β-Actin in cell fragment was served as an internal control. (d) A representative immunofluorescent staining showed that rosiglitazone and 15d-PGJ2 markedly inhibited PAI-1 cytoplasmic staining in cardiac fibroblasts (n=5; bar: 50 μm). (e) Rosiglitazone dose-dependently inhibited Ang II-induced collagen I, collagen III and fibronectin mRNA expression in cardiac fibroblasts. Results are expressed as fold increase over control and mean±s.e.mean data of three independent experiments are shown. *P<0.05 vs control; †P<0.05 vs Ang II; #P<0.05 vs Ang II+Ros or Ang II+15d-PGJ2. Ang II, angiotensin; BADGE, bisphenol A diglycidyl ether; 15d-PGJ2, 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; real-time RT-PCR, real-time reverse transcription-PCR.