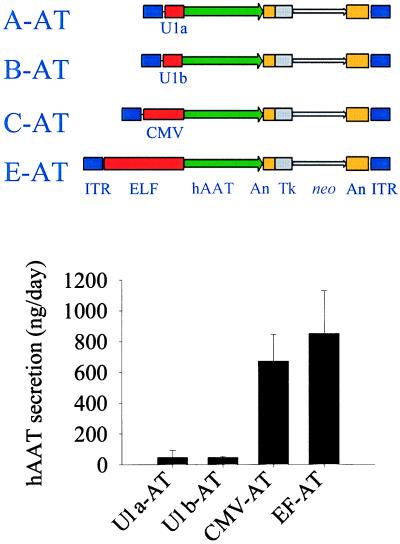
Figure 1.
Transient transfection of C2C12 myoblasts with AAV-AAT. (Upper) Four AAV-AAT vector cassettes. The A-AT and B-AT constructs contain the promoters from the small nuclear RNA genes, U1a and U1b, respectively. The C-AT construct contains the CMV promoter, whereas the E-AT vector uses the human elongation factor 1-α (ELF in the figure) promoter. ITR, AAV inverted terminal repeat; An, polyA signal; Tk, the HSV thymidine kinase promoter; neo, the Tn5 neomycin phosphotransferase gene. (Lower) The rates of secretion from transfected cultures. C-AT does not differ significantly from E-AT, but both differ from A-AT and B-AT (P < 0.05).