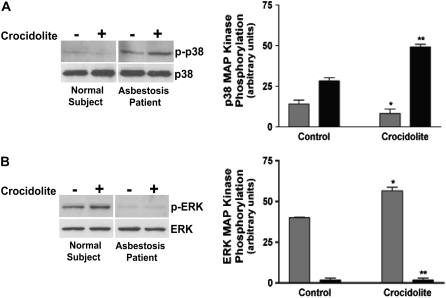
Figure 1.
Alveolar macrophages from patients with asbestosis have constitutive p38 kinase activity and absent extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK) activity compared with normal subjects. Whole cell lysates were prepared from alveolar macrophages obtained from normal subjects (n = 3) or from patients with asbestosis (n = 3) cultured in the presence or absence of crocidolite asbestos. The lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blot analysis was performed with (A) p-p38 and p38 or (B) p-ERK and ERK monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to determine activation and confirm equal loading of proteins, respectively. Representative Western blot analyses are shown. In both A and B, densitometry was performed from the three experiments and is expressed graphically in arbitrary units. For statistical comparisons, in A, * denotes a comparison of p-p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in alveolar macrophages exposed to asbestos from patients with asbestosis and normal subjects (P < 0.0001), and ** denotes a comparison of p-p38 in alveolar macrophages from patients with asbestosis with and without exposure to crocidolite asbestos (P < 0.0007); in B, * denotes a comparison of p-ERK in alveolar macrophages from normal subjects with and without exposure to crocidolite asbestos (P < 0.0083), and ** denotes a comparison of p-ERK in asbestos-exposed alveolar macrophages obtained from patients with asbestosis and normal subjects (P < 0.0010). Shaded bars, normal subjects; solid bars, patients with asbestosis.